Industry Guide
Facilities Management for Educational Facilities

Educational institutions must keep students and staff safe, meet strict regulations, and avoid disruptions to learning and research. Facility management in this setting extends beyond maintenance. It keeps campuses audit-ready, safeguards people and assets, secures sensitive spaces, and maintains continuity of operations. By embedding compliance into daily workflows and strengthening emergency preparedness, facility management helps schools and universities align regulatory requirements with academic goals.
When done well, facility management delivers institution-wide visibility and control across visitor check-in, contractor oversight, access logging, logistics tracking, and coordinated emergency response. The outcome is safer communities, protected assets, uninterrupted learning, and a stronger institutional reputation in competitive education markets.
Summary
Facility management in education keeps institutions safe, compliant, and audit-ready. It protects students, staff, and intellectual property while reducing liability and regulatory risk. By focusing on visitor oversight, contractor compliance, emergency preparedness, asset tracking, and access control, leaders strengthen operational resilience and institutional trust.
Why Facility Management Matters in Education:
-
Ensures compliance with OSHA, ADA, FERPA, the Clery Act, and accreditation standards.
-
Protects people, research assets, and data from risk.
-
Minimizes disruptions to learning and supports continuity of campus operations.
-
Strengthens institutional reputation with parents, students, boards, and regulators.
Core areas of focus: Visitor management, contractor compliance, emergency preparedness, asset and logistics management, and identity and access control.
Compliance connection: Facility management embeds regulatory requirements into daily operations, keeping campuses audit- and accreditation-ready at all times.
Measuring success: Success is tracked through KPIs such as drill performance, audit readiness time, contractor compliance rates, visitor oversight, and asset utilization.

Chapter 1
What Is Facility Management in Education?
Facility management in education coordinates the systems, processes, and teams that keep campuses safe, compliant, efficient, and resilient. It shapes the experience for students, faculty, and staff and influences institutional reputation. Day to day, it controls access to dorms and labs, oversees contractors, maintains safe learning environments, prepares for emergencies, and tracks campus assets to ensure proper use.
Across schools and universities, facility management goes beyond maintenance. It protects people, safeguards intellectual property and research, and sustains operations so learning, research, and campus life continue without disruption.
How Does Facility Management Differ Across Education Settings?
Different types of institutions face unique facility management challenges that shape how they oversee people, assets, and compliance:
Higher Education
Universities run complex, multi-building campuses with residence halls, laboratories, libraries, research centers, and public venues. Facility leaders secure sensitive research spaces, manage visitor check-in for events, and keep residence halls safe.
Kindergarten to 12th Grade (K–12) Schools
Public and private schools balance safety with accessibility. Facility management emphasizes controlled access for students and staff, strict visitor oversight, and preparedness for emergencies such as severe weather or security incidents. Recordkeeping and compliance reporting are essential, particularly in districts with oversight requirements at state or federal levels.
Private & Charter Schools
These institutions may operate with tighter budgets but must demonstrate strong safety and compliance to parents, boards, and regulators. Facility leaders focus on optimizing resources, holding contractors accountable, and providing reliable, secure learning environments.
What Are the Main Goals of Facility Management in Education?
Across all types of educational institutions, facility management serves four essential goals:
Protect People
Provide safe environments for students, faculty, staff, and visitors. Maintain clear emergency procedures, ensure controlled access, and reduce risk across classrooms, labs, and residential areas.
Ensure Compliance
Meet and document adherence to safety, environmental, and accessibility regulations. Keep audit-ready records for standards such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), as well as state board and accreditation requirements.
Safeguard Research & Assets
Protect intellectual property, sensitive data, and high-value equipment such as lab instruments and information technology (IT) infrastructure. Secure specialized facilities and prevent unauthorized access.
Support Continuity of Learning
Minimize downtime by streamlining contractor and vendor access, coordinating rapid response during emergencies, and improving visibility into how space and resources are used.
Together, these goals reinforce safety, compliance, and operational stability while protecting institutional reputation in an increasingly competitive education landscape.

Chapter 2
Why Facility Management Matters in Education
Education leaders work every day to keep campuses safe, welcoming, and compliant while meeting requirements from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and state or federal education boards. A single gap, such as a contractor without proper clearance, a missed visitor check-in, or an emergency with unclear procedures, can create safety risks, regulatory violations, or reputational damage. Facility management provides the oversight that keeps campuses audit-ready, compliant, and resilient.
How Does Facility Management Protect Learning Continuity?
Unplanned disruptions do more than inconvenience students and staff. They interrupt classes, delay research, and can compromise safety. Strong facility management reduces these risks by:
These measures help institutions avoid closures, keep learning on track, and protect both academic schedules and research commitments.
How Does Facility Management Reduce Institutional Risks?
Without effective oversight, schools and universities are exposed to:
Compliance violations that lead to fines, failed inspections, or loss of accreditation or funding.
Safety incidents that put students, staff, and visitors at risk.
Research setbacks from lost data, damaged equipment, or unauthorized access.
Reputational damage that undermines parent trust, student recruitment, and alumni or donor support.
The impact varies by setting. In higher education, research interruptions or compliance failures can jeopardize grants and partnerships. In kindergarten through twelfth grade (K–12), lapses in visitor oversight can create liability and community backlash. In private institutions, even small safety gaps can affect enrollment decisions and parental confidence.
How Does Facility Management Safeguard Compliance & Institutional Reputation?
Compliance is a daily practice, not an event. Facility management embeds controls into routine operations through digital access logs, contractor and vendor records, and visitor management systems. In higher education, that includes demonstrating OSHA and EPA compliance while securing laboratories and research spaces. In K–12, it means consistent visitor oversight, controlled access, and adherence to district and state safety standards. Standardized protocols and complete records reduce risk, protect communities, and sustain the trust that supports enrollment, funding, and long-term reputation.
Educational institutions manage risks that span safety, compliance, and daily operations. Whether you run a large university, a K–12 district, or a private school, facility management provides the structure to protect people, safeguard assets, and keep learning on track.
The core areas of facility management in education are:
- Visitor Management
- Contractor Compliance Management
- Emergency Preparedness
- Asset & Logistics Management
- Identity & Access Management

Chapter 3
Why Do Educational Institutions Need Visitor Management?
Every person entering campus affects safety, compliance, and community trust. Unlike typical offices, schools and universities host students, staff, parents, contractors, auditors, and guests across open, multi-entrance environments. Without structured oversight, risks include unauthorized access, security incidents, liability exposure, and violations of state or federal rules. Consistent visitor protocols reduce threats to student safety, protect research spaces, and support requirements under the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA), and state board policies.
How Do Education Institutions Manage Visitor Check-Ins?
Approaches vary widely depending on institution type and resources:
Paper sign-in sheets common in smaller K–12 schools; inexpensive but error-prone, hard to search, and unreliable for audits or emergencies.
Spreadsheets improve organization but still require manual data entry and lack consistency across sites.
Standalone software allows faster check-ins and better reporting but often operates in silos without linking to access control, or safety systems, or student information systems.
Cloud-based visitor management systems provide real-time visibility of who is on campus, enable pre-registration for events, and integrate with security and compliance tools.
Traditional methods can meet minimum needs. Digital systems make it easier to scale across districts or universities, automate documentation, and stay audit-ready for inspections or drills.
What Are the Core Tasks of Visitor Management in Education?
Most education facilities has to complete several essential visitor management tasks, regardless of whether they use paper, spreadsheets, or cloud software.
Core visitor management tasks:
- Verifying visitor identity and purpose of entry
- Capture required safety acknowledgments or policy confirmations before access
- Issue badges or passes that limit access to appropriate areas
- Recording arrivals and departures accurately
- Maintain searchable logs for audits, investigations, and emergencies
When supported by technology, these tasks extend further:
- Pre-register and approve high-volume groups for orientations, conferences, or sport games
- Screen against configured watchlists to prevent high-risk entry
- Collect digital acknowledgments for policies such as lab safety or nondisclosure in research spaces
- Monitor real-time dashboards to see who is on campus across sites
- Automate sign-out and reporting to keep records current

How Does Visitor Management Support Compliance and Safety?
K–12 schools often must follow state mandates for identification and sign-in. Universities need to demonstrate OSHA and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) compliance in labs and facilities, and to protect student data under FERPA.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 45001 also treats visitor oversight as part of broader health and safety management. For institutions involved in sensitive or government-funded research, detailed visitor logs help demonstrate physical security and intellectual property safeguards.
Digitizing these processes replace paper with searchable logs, automated checks, and complete audit trails for inspectors, boards, and families.
How Can Education Institutions Set Up Visitor Check-Ins Effectively?
Implementing visitor management requires a structured process that can be applied consistently across campuses:
- Define visitor categories (auditors, vendors, event guests) and assign risk levels.
- Require pre-registration and approvals for higher-risk groups.
- Establish site-specific safety acknowledgments or training for regulated zones.
- Configure badge rules for time limits, restricted zones, and escort rules where needed.
- Standardize sign-out and reporting procedures to keep records audit-ready.
A structured process keeps screening consistent and supports both daily operations and visitor oversight.
? FAQs for Visitor Management in Education
What counts as a visitor on campus?
Anyone who is not a student, faculty member, or staff member, including parents, vendors, contractors, auditors, and event guests.
Do visitors need safety training or acknowledgments?
Yes. Depending on the destination, visitors may need to complete policy acknowledgments before entering areas such as laboratories, athletic facilities, or residence halls.
How long should visitor records be kept?
Follow state requirements and institutional policy. Retain records long enough to satisfy board reviews, legal obligations, or grant audits.
How does visitor management support emergencies?
Accurate visitor logs feed mustering tools so all people on campus, including non-students, are accounted for during drills and incidents.
Why are paper sign-in sheets risky in education?
They are easy to misplace, slow to verify, and unreliable during emergencies or audits, especially across multi-building campuses.
Why are cloud-based visitor systems preferred?
They provide real-time oversight, integrate with access control and student systems, and produce reliable, searchable audit trails across campuses or districts.

Chapter 4
Why Do Education Institutions Need Contractor Compliance Management?
Contractor compliance management ensures every vendor, service provider, and contractor on campus meets safety, credentialing, and insurance requirements before work begins. Contractors often handle high-risk tasks, from laboratory and information technology maintenance to construction, food service, and transportation. If certifications, background checks, or insurance lapse, institutions face OSHA violations, failed inspections, liability claims, and potential safety incidents. Centralized oversight reduces these risks and creates clear, audit-ready proof that standards were enforced.
How Do Education Facilities Manage Contractor Compliance Documentation?
Contractor compliance documentation is managed in several ways, depending on an institution’s resources and maturity of its processes:
Some schools still rely on binders or file cabinets to store contractor credentials. This approach is prone to lost documents, inconsistent updates, and long retrieval times during audits.
Others track expirations and requirements in spreadsheets or Excel, which allows for more organization but requires manual follow-up, is error-prone, and becomes unmanageable across multi-building campuses.
Standalone software or desktop tools provide more structure for tracking documents, but often lack automation or integration with site check-in systems.
Cloud-based contractor compliance management systems centralize all contractor documents, automate reminders for expiring certifications, and link compliance status directly to site access, ensuring only approved contractors can check-in.
Paper and spreadsheets can meet basics. Digital tools scale across districts and campuses and deliver instant evidence of compliance.
What Are the Core Tasks of Contractor Compliance in Education?
Contractor compliance management revolves around making sure that every outside worker is properly documented and cleared before entering a site.
Core contractor-compliance tasks:
- Collect, store, and verify licenses, insurance, safety certs, and training.
- Configure approval workflows, flag gaps or expirations, and keep an audit trail.
- Set site-specific requirements by contractor type and risk.
- Track expiration dates with reminders to contractors and facility teams.
- Link compliance status to check-in so only approved contractors access the site.
When supported by technology, these tasks extend further:
- Guided document submission plus review and approvals, with full audit trail.
- Automated expiration tracking with real-time notifications to prevent lapses.
- Central dashboards and cross-site visibility into vendor and contractor status.
- Visitor management system integration to auto-approve at sign-in for fast, authorized check-ins.
- Audit-ready recordkeeping with complete, time-stamped history.

How Does Contractor Compliance Management Support Regulations & Standards?
Contractor oversight protects safety, funding, and trust. OSHA requires proper training and documentation for contracted work in labs, maintenance, and construction areas. State and district rules often mandate background checks for anyone working around students. Universities engaged in government-funded research must ensure contractors meet clearance and security protocols before accessing labs or data centers.
International frameworks reinforce these practices: ISO 45001 emphasizes consistent health and safety oversight for all worker categories, and ISO 9001 requires accurate, retrievable documentation. Centralized contractor records help institutions prove every outside worker was vetted and approved, reducing liability, compliance failures, and community concerns.
How Can Education Facilities Set Up Contractor Compliance Effectively?
A strong contractor compliance program is built on clear requirements and automated enforcement:
- Define contractor categories and risk levels (e.g. custodial staff, information technology vendors, construction crews, food service providers).
- Establish standardized approval workflows with expiration rules and automated reminders.
- Require digital submission of documents and training records to reduce manual tracking.
- Integrate compliance status directly to check-in systems so only compliant contractors gain access.
- Maintain audit-ready reports and handle exceptions consistently for inspections or board reviews.
This approach ensures contractors are not just managed at the project level but are consistently vetted and documented across the entire facility.
? FAQs for Contractor Compliance in Education
What documents are typically required from contractors?
Background checks, proof of insurance, safety certifications, licenses, and role-specific training.
How do multi-campus universities or districts maintain consistent standards?
Centralize requirements in a shared system and allow sites to add local rules when needed.
How can contractors clear access faster?
Keep documentation current and pre-approved so check-in is quick with fewer escalations.
How is audit readiness maintained?
Audit readiness is maintained by keeping a digital trail of all documents, approvals, rejections, and expirations, making it easy to export evidence for inspectors.
Why are spreadsheets and paper records risky?
They rely on manual follow-up, are difficult to standardize across sites, and make it challenging to prove compliance during audits.
Why are cloud-based systems preferred for contractor compliance management?
Automation for expirations, dashboards for status, and direct links to access control make oversight scalable and reliable.
Explore More Contractor Compliance Management Resources

Chapter 5
Why Do Education Institutions Need Emergency Management & Preparedness?
Campuses face a wide range of risks, from fires, severe weather, and medical emergencies to active threats and infrastructure failures. Schools and universities must account for students, faculty, and staff, plus contractors, parents, and visitors who may not know your procedures. A structured emergency management program makes sure everyone on-site can be alerted, evacuated, and accounted for quickly, and that you have the documented proof regulators, boards, and accreditors expect.
How Do Education Facilities Manage Emergencies and Preparedness?
Education facilities manage emergencies by combining defined procedures with tools that improve speed and accountability. Methods vary by facility, ranging from paper rosters and radio calls to spreadsheets, desktop software, and modern cloud-based emergency management systems. Each approach offers different levels of accuracy, visibility, and compliance support.
Paper rosters & radio check-ins remain common in some facilities. They are inexpensive but slow, error prone, and hard to audit.
Spreadsheets improve organization but still require manual data entry and lack consistency across multiple sites.
Standalone software speeds alerts and musters but often operates in silos without linking to access control or visitor systems.
Cloud-based emergency systems provide centralized oversight, real-time evacuation tracking, mass notifications, and integration with security and compliance tools.
While older methods can meet basic needs, digital platforms make it easier to scale across multi-building campuses, reduce response times, and provide proof of compliance during inspections.
What Are the Core Tasks of Emergency Management in Education?
At minimum, plan for emergencies, document drills, and account for every person on campus:
Core emergency preparedness tasks:
- Defining emergency roles and responsibilities for supervisors, floor leaders, and safety officers
- Mapping muster points and building sweep routes across campus
- Scheduling and documenting drills to meet regulatory requirements
- Capturing attendance, headcounts, response times, and all-clear confirmations
- Reviewing drill and incident performance to identify gaps and corrective actions
When supported by technology, these tasks extend further:
- Automated mass notifications with two-way messaging via SMS, email, or calls
- Real-time digital musters and roll calls across multiple muster points
- Live dashboards showing who is on premise across one or many buildings
- Reconciliation of headcounts with access control and sign-in data
- Exportable drill and incident reports to ensure records remain current

How Does Emergency Management Support Compliance & Safety?
Emergency management demonstrates that institutions can protect people and maintain learning continuity during incidents. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) requires Emergency Action Plans. Many states mandate lockdown or severe weather drills in kindergarten through twelfth grade (K–12).
Universities must also meet OSHA, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and Clery Act reporting requirements, including proof that procedures are tested and communicated.
International standards reinforce this. International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 45001 emphasizes emergency preparedness, and ISO 9001 requires documented, tested, and continuously improved procedures. Centralized processes and records show how drills were run, how quickly people were accounted for, and how performance improved over time.
How Can Educators Set Up Emergency Preparedness Effectively?
Building an effective program requires both planning and practice:
- Define emergency scenarios specific to each campus and document clear procedures.
- Assign roles and responsibilities for administrators, faculty, staff, and student leaders.
- Communicate muster points and establish digital roll call processes.
- Schedule and document drills that align with state and federal requirements.
- Review trends across sites and refine procedures to close gaps and strengthen future preparedness.
This approach ensures that emergency preparedness is not a one-time exercise but a continuous, auditable process.
? FAQs for Emergency Management in Education
How do schools and universities account for visitors during an evacuation?
Integrate visitor and contractor records with emergency systems so they appear in real-time alerts and roll calls.
What records should be kept for audits or board reviews?
Maintain digital evacuation logs, drill reports, attendance data, and time-to-clear metrics by building and scenario.
How often should drills be conducted?
Follow state and federal rules. K–12 schools may need multiple drills per year. Universities align with OSHA, the Clery Act, and institutional policy.
Can emergency procedures vary by scenario?
Yes. Tailor workflows for fires, severe weather, medical emergencies, and active threats with scenario-specific messages and roles.
Why are manual roll calls risky in education?
Paper lists are often incomplete or inaccurate during large, multi-building events, which weakens both safety and compliance.
Why are digital systems becoming the standard?
They improve accountability, reduce human error, and provide exportable records that support both compliance reviews and institutional reporting.
Explore More Emergency Management Resources

Chapter 6
Why Do Educational Institutions Need Asset and Logistics Management?
Every day, campuses move resources, equipment, and deliveries. From classroom technology and laboratory instruments to maintenance tools and vendor shipments, each handoff can introduce error, delay, or loss. Poor oversight disrupts classes, misplaces equipment, wastes budget, and can create safety issues. Weak logistics create bottlenecks at docks, mailrooms, and storage areas.
Standardizing asset tracking and logistics flow ensures the right items reach the right place at the right time, with a clear chain of custody for audits and investigations.
How Do Educational Institutions Manage Assets and Logistics?
Institutions manage assets and logistics with a mix of manual and digital methods that vary by scale and maturity:
Paper logs and clipboards are still common for recording tool check-outs or deliveries, but prone to errors, loss, and illegible handwriting.
Spreadsheets offer better organization but require manual updates, which become unreliable as facilities scale.
Legacy point solutions provide digital tracking for specific workflows like mailrooms, but often operate in isolation from other systems.
Cloud-based asset and logistics systems centralize receiving, storage, usage, and distribution, integrate with ERP, student information, and work orders, and use barcodes to monitor location, condition, and movement in real-time.
Facilities that rely on manual processes often struggle during audits and recalls, while those using integrated digital tools gain real-time visibility and standardized reporting across multiple plants.
What Are the Core Tasks of Asset and Package Tracking in Education?
Effective management spans the entire lifecycle of items on campus.
Core asset & logistics tasks:
- Receiving inbound items, scheduling docks, and checking in drivers
- Tracking lots and batches to maintain chain of custody through use or shipment
- Controlling storage zones and restricted areas for regulated or high-value items
- Managing tools and equipment with check-in/out workflows
- Monitoring conditions for sensitive materials, preparing shipments with accurate labeling, and capturing exceptions
When supported by technology, these tasks extend further:
- Central receiving with purchase order line-item receiving to verify and close POs in one screen.
- Real-time visibility and chain-of-custody tracking for each item across sites.
- Digital proof of delivery using signatures and photo verification.
- Real-time notifications and alerts to recipients and teams.
- Integrations with ERP platforms and intelligent lockers to streamline handoffs and records.

How Does Asset and Package Tracking Support Compliance?
Institutions must show not only what they purchased, but how items were handled, stored, and distributed. OSHA governs safe storage and transport of chemicals. The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) and information technology (IT) policies require oversight of devices that hold student data. Research programs may mandate strict chain-of-custody for grant-funded equipment, samples, or specialized materials.
ISO 9001 calls for documented, traceable resource management, and ISO 45001 highlights safe handling and storage. Centralized records help institutions demonstrate compliance, speed audits, and reduce risk tied to mismanaged assets.
How Can Education Logistics Set Up Asset and Logistics Tracking Effectively?
A structured program ensures resources move through campuses securely and efficiently:
- Define item categories (IT devices, lab materials, maintenance tools, vendor deliveries) and assign ownership rules.
- Map storage zones and movement paths, and track transfers with digital proof of movement.
- Standardize receiving, movement, and check-in/out with barcode-based workflows, notifications, and purchase-order line-item receiving.
- Implement traceability with barcode scanning and PO linkage to maintain chain of custody from intake to delivery.
- Connect to your ERP, lockers, and other logistics systems, then use real-time dashboards and alerts for centralized reporting and exceptions; add temperature monitoring where required.
This approach creates a repeatable, auditable process that reduces losses, improves utilization, and strengthens accountability.
? FAQs for Asset and Logistics Management in Education
What is the difference between assets and supplies in education?
Assets are durable items such as laptops, lab equipment, and AV tools. Supplies include consumables like textbooks, paper, and lab chemicals.
How do institutions track shared or loaned equipment?
Check-in/out workflows with due dates, condition notes, and reminders reduce loss and ensure accountability.
Do campuses need mobile scanning?
Yes. Barcode, QR, or RFID scanning improves accuracy, speeds up receiving and check-out, and ensures movements are logged in real-time.
Why are paper logs risky for schools and universities?
They are error-prone, time-consuming to search, and unreliable when auditors or boards require accurate, complete records.
Why are cloud-based logistics platforms preferred?
They integrate with campus systems, provide real-time visibility, and generate reliable, searchable records across multiple buildings and campuses.

Chapter 7
Why Do Educational Institutions Need Identity & Access Management?
Identity and access management protects students, staff, and assets by making sure only the right people enter specific areas at the right time. Campuses include dormitories, laboratories, data centers, athletic facilities, and administrative offices, each with different access needs.
Without structured controls, unauthorized entry can lead to safety incidents, theft, vandalism, data breaches, and regulatory violations. A well-managed program also creates the documentation boards, regulators, and auditors expect, proving that permissions were assigned, reviewed, and enforced properly.
How Do Educational Institutions Manage Identity and Access?
Identity and access management in education is handled through a mix of manual and digital systems that vary by institution size and complexity:
Manual sign-in and key distribution is still used in smaller sites, but risky due to lost keys, lack of tracking, and no audit trail.
Standalone badge systems provide basic access controls, but often lack integration with HR systems or visitor check-ins.
On-premise PIAM solutions assign permissions more systematically, but can be difficult to scale across multiple sites.
Cloud-based identity and access management systems automate provisioning, enforce role- and zone-based permissions, making compliance and oversight easier.
While manual and legacy systems can cover basic needs, digital platforms provide centralized control, ensure least-privilege access, and simplify audits.
What Are the Core Tasks of PIAM in Education?
Most education facilities need to complete several essential identity and access tasks, regardless of whether they use paper logs, spreadsheets, or cloud software:
Core identity and access management tasks:
- Verify identities and pre-approve employees, contractors, and visitors.
- Assign role- and zone-based permissions aligned to risk.
- Issue and manage temporary credentials with time and area limits.
- Monitor access activity and maintain audit records.
- Review permissions periodically and revoke access when it’s no longer appropriate.
When supported by technology integrated with visitor management, these tasks extend further:
- Automate credential issuance and permission provisioning with rule-based workflows, tied to visitor management checks like approvals and watchlists.
- Set precise time-bound and area-specific access levels, with credentials that can auto-expire on sign-out or after a set duration.
- Issue digital credentials as QR codes at the kiosk and by email so guests can access gates without badge printers.
- Integrate with access control systems and use real-time reporting and centralized administration to see who accessed what, when, across sites.
- Automated sign-out and reporting to ensure records remain current.

How Does Access Management Support Compliance and Safety?
Access control is fundamental to compliance and student safety. For K–12, many states require that only authorized individuals enter school buildings during instructional hours.
Universities must show compliance with OSHA, the Clery Act, and EPA rules, which limit hazardous areas to trained personnel and require accountability during emergencies. FERPA underscores protecting data and information technology spaces with strict access controls.
ISO 45001 links access oversight to worker safety, and ISO 9001 emphasizes consistent documentation of permissions. Centralized approvals and accurate records show that every access decision was authorized, justified, and auditable.
How Can Campuses Set Up PIAM Effectively?
Setting up an effective access management program requires both policy and technology:
- Define access profiles with specific areas, times, and durations, then use rule-based workflows to automate who gets which permissions.
- Tie credential issuance to visitor management checks so approvals and watchlists must pass before access is granted.
- Choose credential types and expirations that fit the scenario, including digital QR credentials issued from the kiosk or by email, with options to expire on sign-out or after a set time.
- Integrate with your access control system to apply permissions at doors, turnstiles, gates, and more, while keeping everything centrally managed.
- Use real-time reporting and audit logs to review who accessed which points, when, and to support periodic access reviews and revocations.
This approach prevents access creep, tightens security at sensitive zones, and leaves a clear, audit-ready record of how access decisions were made.
? FAQs for PIAM in Education
What is PIAM in an education context?
PIAM (physical identity and access management) is a system that manages identities, credentials, and permissions across campuses, applying role- and zone-based rules.
How do schools or universities handle temporary visitors, contractors, or auditors?
They are issued time-bound, zone-restricted badges tied to verified prerequisites and, when needed, escorted by staff.
How long should access logs be retained?
Retention depends on state law and institutional policy. Logs should be kept long enough to satisfy Clery Act, OSHA, or accreditation requirements.
How do institutions reduce access violations?
By enforcing least-privilege permissions, conducting proactive access reviews, and monitoring real-time alerts for unauthorized activity.
Why are manual systems risky for access control?
Manual logs or physical keys lack reliable records, are prone to misuse, and make compliance difficult to prove during audits.
Why are cloud-based access systems increasingly preferred?
They centralize oversight, integrate with HR and student systems, enforce consistent policies across campuses, and provide searchable audit trails that meet regulatory and security requirements.

Chapter 8
Compliance and the Regulatory Landscape
Educational institutions must follow strict regulations that vary by setting and geography. Facility management provides the structure, documentation, and daily oversight needed to stay compliant, reduce risk, and remain audit-ready. The table below outlines key regulations across different education settings and what they mean in practice.
Higher Education
Main Focus: Campus safety, lab oversight, emergency readiness, data security.
|
United States |
Canada |
Global |
|
Clery Act – Campus crime reporting and emergency notifications. FERPA – Protection of student education records. OSHA/EPA – Lab safety, hazardous material handling, and environmental compliance. OSHA – Workplace health and safety. |
PIPEDA – Data protection and privacy. CCOHS – Workplace health and safety. Health Canada – Oversight of lab and environmental safety. |
ISO 45001 – International workplace safety. ISO 27001 – Information security management for data and IT. ISO 9001 – Quality management for institutional operations. |
K–12 Schools
Main Focus: Student safety, visitor oversight, accessibility compliance.
|
United States |
Canada |
Global |
|
State education codes – Mandated drills, visitor check-in, and facility safety. OSHA – Staff safety and training standards. ADA – Accessibility requirements for buildings. |
Provincial education acts – Facility safety and mandated emergency procedures. CCOHS – Staff workplace health and safety. |
UNICEF Child Protection Standards – Global guidance for safe schools. ISO 21001 – Educational organization management systems. |
Private / Charter Schools
Main Focus: Student safety risk reduction, liability protection, emergency preparedness
|
United States |
Canada |
Global |
|
Accreditation requirements – Independent school associations require documentation of facility safety and emergency plans. Insurance-driven compliance – Liability standards tied to contractor and vendor oversight. |
Private school acts (provincial) – Require facility accountability for safety and operations. |
ISO 31000 – Risk management framework. |

Why Is Compliance Tied to Facility Management?
Compliance is tied to facility management in education because the systems that oversee visitors, contractors, emergencies, assets, and access generate the records that school boards, state departments of education, accrediting bodies, and federal regulators require. Every regulation affecting K–12 schools, universities, and research institutions expects proof that campuses are safe, secure, and under control.
By embedding compliance into daily facility operations, educational institutions can turn regulatory requirements into structured workflows that keep campuses audit-ready, protect institutional reputation, and demonstrate accountability to parents, students, boards, funders, and regulators. Strong facility systems also make it easier for schools and universities to adopt digital tools that strengthen compliance over time.

Chapter 9
Technology & Digital Transformation in Facility Management
Now that we have covered core areas, compliance needs, and best practices, let's look at the tools that make this work easier. This chapter explains how campuses are shifting from manual processes to digital systems, and how to design the right performance measures so you can prove progress and improve every term.
How Is Facility Management Shifting from Manual to Digital?
Many institutions still use paper logs, spreadsheets, and sign-in books for important tasks. These methods slow response, increase human error, and make compliance hard to prove as campuses grow.
Typical pain points:
- Visitor oversight: Paper sign-ins that are hard to search during audits or emergencies
- Emergency drills: Clipboards and manual roll calls that miss people and delay all-clear times
- Assets and packages: Misplaced deliveries in residence halls and lost classroom devices
- Contractor compliance: Expiring credentials tracked in email or spreadsheets
- Access control: Standalone systems that do not sync with human resources (HR) or student information systems
Campuses are moving to cloud platforms that structure workflows, keep records audit-ready, and give leaders real-time visibility.
What Are the Benefits of Facility Management Software?
The benefits of digital transformation in facility management include automating compliance tasks, improving visibility, and keeping institutions audit-ready at all times. Moving from paper and spreadsheets to digital platforms fundamentally changes how campuses manage both compliance and daily operations.
Automated Compliance Workflows
Routine tasks such as verifying contractor certifications, sending visitor training modules, or preparing audit reports can run automatically instead of relying on manual tracking.
Analytics for Improvement
Facilities can track response times during drills, identify trends in incident reports, and use data to close safety or compliance gaps before they escalate.
Connected Systems
When EHS, quality, and security systems share information, it reduces duplicate work and gives teams a clearer picture of risks and compliance status.
Audit-Ready Records
Digital logs make it easier to show regulators proof of compliance with your required regulatory standards.
Predictive Insights
Advanced tools can flag recurring issues, forecast risks, and help facilities take action before disruptions or non-compliance occur.
Why Does Facility Management Software Matter for Education?
Software does not replace your procedures. It strengthens them. Digital platforms help schools and universities stay compliant while making daily work easier to manage. Instead of scrambling before an inspection, you can continuously track who is on campus, verify contractor approvals, monitor drills, and oversee assets and packages in real time. In a setting where safety, accountability, and compliance are always under scrutiny, modern tools provide the structure to protect people, secure resources, and support long-term institutional resilience.
One platform that addresses these needs is FacilityOS, which offers modular solutions for visitor management (VisitorOS), emergency and evacuation management (EmergencyOS), contractor compliance (ContractorOS), asset and logistics management (LogisticsOS), and physical identity and access management (SecurityOS). Educational institutions can start with one module and expand as their needs evolve, ensuring scalability across single campuses or entire districts while maintaining a unified user experience and centralized reporting.
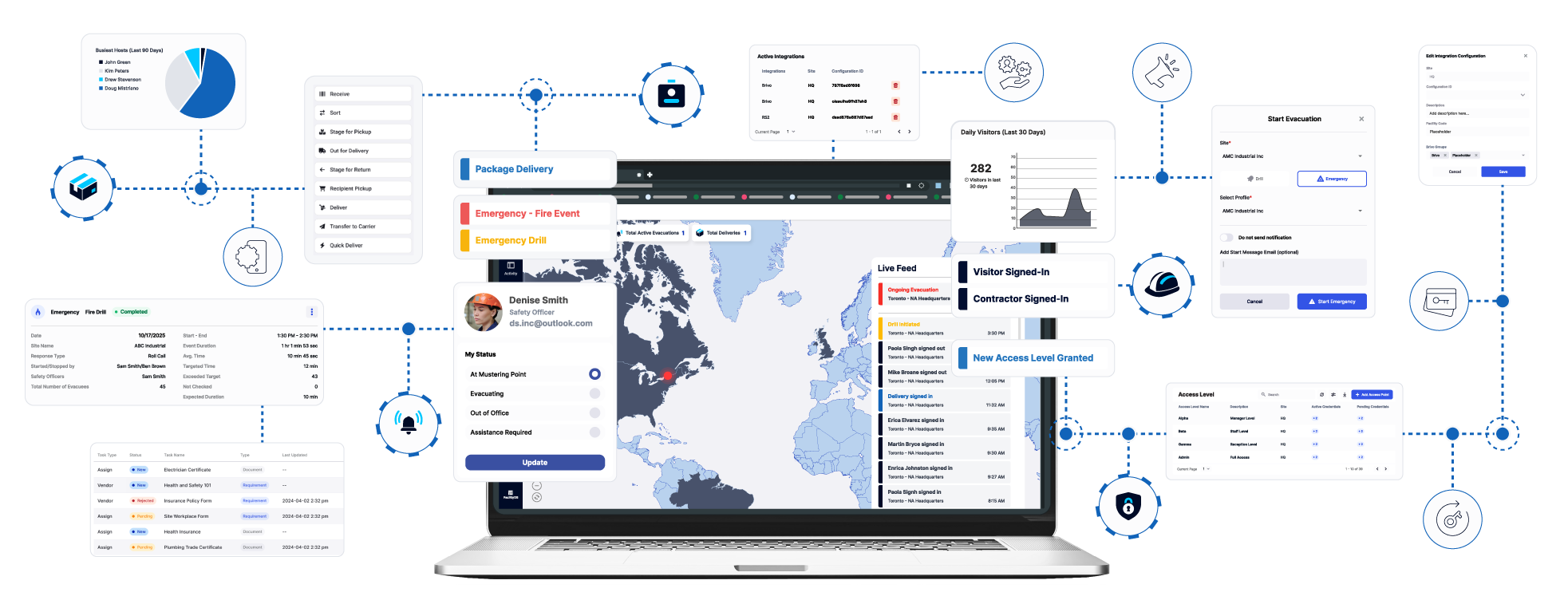
Explore More Technology Resources

Chapter 10
Measuring Success: KPIs for Facility Management
Measuring results is essential to show whether facility management efforts are effective. In education, this means tracking indicators tied to safety, compliance, and continuity of learning. Clear key performance indicators (KPIs) give schools and universities a way to monitor progress, identify gaps, and remain prepared for audits, inspections, or accreditation reviews.
What Are Key KPIs in Facility Management for Education?
Facility management KPIs provide education leaders with a clear way to measure compliance, safety, efficiency, and visibility across their operations. build performance measures that match your risks, goals, and workflows. Use this approach:
Define Outcomes & Requirements
Identify key results (fewer incidents, faster evacuations, audit readiness) and link them to applicable regulations like OSHA, ADA, FERPA, and Clery Act.
Map Workflows
Connect outcomes to the processes that drive them: visitor check-in, contractor credentialing, emergency drills, access control, and logistics tracking.
Select Metrics
Choose leading indicators (% visitors pre-registered, % drills completed on time) and lagging indicators (evacuation times, access violations) that you can capture automatically.
Set Definitions & Targets
Write clear definitions, assign owners, establish thresholds, and set goals by building, department, or campus type.
Pilot and Refine.
Test metrics at one site, confirm they respond to process improvements, and retire any that don't drive action.
Standardize & Improve
Roll out common metrics across locations, review regularly in safety committees, and assign corrective actions to demonstrate continuous improvement.
Quick test: A KPI is useful if a facilities lead or department head can explain how to improve it today and if the data is available in real-time.
Why Are KPIs Important in Facility Management?
KPIs give schools and universities a clear picture of how well their campuses are meeting safety, compliance, and operational goals. They confirm that emergency drills are effective, show whether contractor oversight is working, and verify that student and staff safety protocols are being followed consistently. Instead of relying on assumptions, superintendents, facility directors, and campus administrators can use data to justify budget requests, demonstrate due diligence to school boards and accreditors, and prioritize improvements that directly protect students, faculty, and staff.
How Do KPIs Show ROI in Facility Management?
KPIs help education leaders demonstrate the return on investment from strong facility management practices. Lower incident rates reduce liability exposure and insurance premiums, faster preparation for accreditation site visits saves administrative time, and consistent regulatory compliance helps institutions avoid state fines, federal penalties, or loss of grant funding. Together, these results show that modern, digital facility management systems not only support student and staff safety but also strengthen institutional reputation, operational continuity, and community trust.

Chapter 11
Future of Facility Management in Education
Educational institutions are increasingly leveraging data and connected systems to enhance safety, compliance, and operational efficiency. The future of facility management in education will be defined by continuous compliance practices, AI-driven insights, and integrated platforms that provide schools and universities with real-time campus visibility while maintaining audit- and accreditation-readiness.
What Is Continuous Compliance in Education Facility Management?
Continuous compliance in education means maintaining institutions in a state of perpetual audit-readiness — eliminating the scramble when inspections, accreditation reviews, or regulatory evaluations are scheduled. Digital facility management systems enable schools and universities to monitor risks continuously, identify recurring compliance issues such as expired contractor credentials or incomplete emergency drills, and resolve them proactively before they escalate into violations.
This proactive approach reduces institutional liability, conserves valuable administrative time, and ensures that learning and research activities proceed without compliance-related disruptions.
How Can AI Improve Facility Management in Education?
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing facility management in education by analyzing institutional data to identify risks, optimize operations, and strengthen compliance frameworks. Rather than depending solely on manual reporting and retrospective analysis, AI uncovers hidden patterns in campus operations and generates actionable recommendations for improvement.
AI applications in educational facility management include:
- Identifying safety vulnerabilities through analysis of incident reports and evacuation drill outcomes.
- Maximizing resource allocation by revealing underutilized classrooms, laboratories, or equipment
- Strengthening campus security by detecting anomalous access patterns or unusual visitor activity.
- Advancing sustainability initiatives by pinpointing energy inefficiencies across facilities.
Through AI implementation, schools and universities can convert raw operational data into strategic insights that enhance safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance. These advantages multiply when facility management systems are fully integrated, as AI algorithms perform best with consistent, real-time data streams.
What Is System Integration in Education Facility Management?
System integration in education facility management refers to connecting visitor management, contractor compliance, emergency response, and access control platforms so they exchange data seamlessly in real time. This integration eliminates operational silos, streamlines daily workflows, and simplifies compliance demonstration during audits, accreditation site visits, or board oversight reviews.
Practical applications of system integration include:
- Automating visitor registration workflows and parent sign-in procedures for enhanced campus security.
- Validating contractor credentials against institutional compliance requirements before access authorization.
- Synchronizing student information systems and HR platforms with physical access permissions for dormitories, research labs, or athletic facilities.
- Linking emergency management platforms with visitor and contractor databases to ensure comprehensive accountability during evacuations.
Through system integration, educational institutions minimize human error, accelerate emergency response times, and maintain comprehensive visibility into campus occupancy and resource utilization. Integration also establishes the data infrastructure necessary for AI-powered analytics that drive continuous improvement and strategic decision-making.
Conclusion
Closing Thoughts on Facility Management in Education
Educational institutions operate in environments where safety, regulatory compliance, and institutional accountability are non-negotiable priorities. Effective facility management provides the operational framework that protects students, staff, and visitors while ensuring uninterrupted learning, research excellence, and vibrant campus life.
Robust processes supported by modern digital tools deliver enhanced operational visibility, streamlined logistics workflows, and simplified compliance with state, federal, and accreditation mandates. These systems reduce audit disruption, ensure proper documentation of emergency preparedness drills, and verify that only authorized individuals access sensitive areas including research laboratories, student housing, and administrative offices.
By investing in integrated, well-documented facility management practices, schools and universities achieve outcomes that extend far beyond regulatory checkbox compliance. They cultivate community trust, improve operational efficiency, and build organizational resilience against both routine operational challenges and unforeseen emergency events.
Institutions that embrace comprehensive facility management are optimally positioned to protect institutional reputation, secure continued funding, and deliver safe, uninterrupted educational excellence in an increasingly complex and scrutinized regulatory environment.
? FAQs About Facility Management in Education
How does maintenance fit into facility management?
Maintenance is one part of facility management, but not the whole picture. Facility management also includes safety oversight, regulatory compliance, visitor and contractor management, emergency preparedness, asset tracking, and access control. While maintenance keeps buildings and equipment running, facility management ensures the entire campus remains safe, compliant, and audit-ready.
What roles are involved in facility management operations at schools and universities?
Facility management in education touches multiple roles.
A Facility Manager or Director of Operations oversees daily site or campus functions.
An EHS or Safety Officer focuses on health, safety, and regulatory compliance.
Security Officers manage access control and protect people, data, and research assets.
Logistics or Asset Managers track the movement of IT equipment, lab materials, and campus deliveries.
Together, these roles coordinate to keep institutions safe, compliant, and efficient.
What technology is recommended for facility management in education?
Modern facility management benefits most from integrated digital platforms that replace manual checklists and paper records. A modular system like the FacilityOS modular platform allows institutions to manage key areas — visitor check-ins (VisitorOS), contractor compliance (ContractorOS), emergency preparedness (EmergencyOS), access control (SecurityOS), and logistics and asset tracking (LogsiticsOS)— all within one platform.
This approach reduces compliance gaps, keeps plants audit-ready, and provides real-time visibility across the facility.


