Industry Guide
Facility Management in Healthcare

Facility management in healthcare is the coordinated work that keeps clinical environments safe, compliant, and ready, so care can happen without delays. It spans buildings and utilities, patient-facing spaces and back-of-house areas, and the day-to-day workflows that support staff, patients, and visitors across hospitals, ambulatory sites, and long-term care.
Healthcare operations rely on constant coordination between staff, visitors, vendors, and emergency teams. Yet most facilities still manage these movements with paper logs, spreadsheets, and manual calls. Modern facility management now depends on connected, digital processes that protect compliance and safety while reducing administrative work.
Because the stakes are patient flow and continuity of care, strong facility processes protect on-time surgeries, ease pressure in emergency departments, and keep imaging and procedure areas available when they are needed.
Summary
Facility management in healthcare protects people, preserves care continuity, and keeps organizations ready for review. The work is practical: standardize key processes, keep environments stable, document activity clearly, and surface issues in real time across sites.
Why Facility Management Matters in Healthcare:
-
Simplifies the way people, deliveries, and contractors enter and move through healthcare spaces.
-
Creates clear records for surveys, audits, and inspections.
-
Reduces administrative effort by automating sign-in, tracking, and communication tasks.
-
Ensures accountability during emergencies and drills.
-
Strengthens community trust through consistent safety standards.
Core areas of focus: Visitor management, contractor compliance, emergency preparedness, asset and logistics management, and identity and access control.
Compliance connection: Facility management embeds regulatory requirements into daily operations, keeping hospitals and clinics audit-ready at all times.
Measuring success: Success is tracked through KPIs such as drill performance, audit readiness time, contractor compliance rates, visitor oversight, and asset utilization.
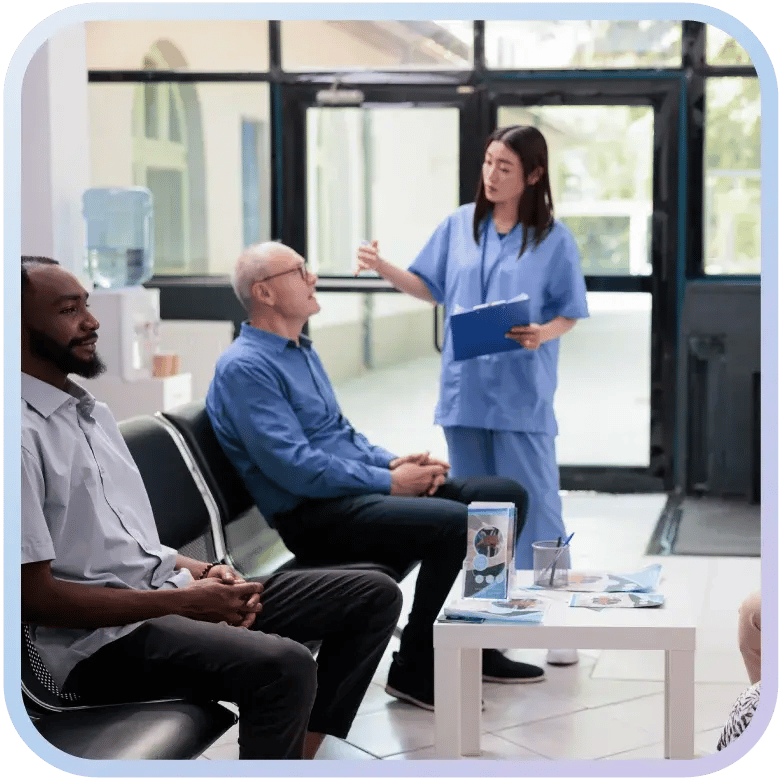

Chapter 1
What Is Facility Management in Healthcare?
Facility management in healthcare is the practice of coordinating people, credentials, assets, and site access to protect the environment of care. Unlike other industries, healthcare facilities require specialized management because patient safety and care delivery depend on secure and uninterrupted operations.
How Does Facility Management Differ Across Healthcare Sectors?
Facility management takes on different responsibilities across healthcare environments, shaped by the type of care delivered and the compliance standards each facility must meet:
Hospitals & Acute Care Centers
Facility management ensures operating rooms, ICUs, and emergency departments remain fully functional. Oversight includes Controlling high-risk zones and maintaining real-time awareness of who is on-site.
Outpatient Clinics & Dental Offices
In smaller, high-turnover environments, facility management focuses on managing high-volume and short-visit traffic efficiently, infection control in treatment rooms, and medical waste handling.
Long-Term Care & Elderly Services
Facility managers prioritize resident safety through fall prevention measures, secure access points, and evacuation plans adapted for patients with limited mobility. They coordinate with staff to comply with CMS requirements and state-level care regulations, while supporting a comfortable living environment.
Mental Health & Rehabilitation Facilities
Facility management emphasizes safe, controlled spaces for therapy and recovery. This includes secure and monitored access to sensitive areas. Practices are designed to protect both patients and staff while fostering therapeutic settings.
Medical Laboratories & Imaging Centers
Facility leaders maintain strict chain-of-custody for samples, biosafety compliance, and scheduled calibration of diagnostic equipment. They manage access controls for restricted labs and ensure that imaging machines and testing devices are available and reliable at all times.
Blood & Organ Banks
Facility management covers refrigeration and environmental monitoring systems that safeguard life-saving inventories. Access controls, FDA compliance checks, and chain-of-custody procedures ensure every unit of blood or organ is stored safely, traceable, and ready for use.
What Are the Main Goals of Facility Management in Healthcare?
Across all types of healthcare institutions, facility management serves four essential goals:
Protect Patients & Staff
Provide safe environments for patients, staff, and visitors. Maintain clear emergency procedures, ensure controlled access, and reduce risk across clinics, labs, and restricted areas.
Ensure Compliance
Maintaining compliance with federal, state, and accreditation requirements that govern healthcare operations.
Promoting Efficiency & Sustainability
Promoting efficiency and sustainability through better use of resources, removing paper-based tasks, and reduced downtime.
Continuity of Care
Ensuring continuity of care by keeping track of the movement of essential equipment and life-supporting systems, ensuring smooth visitor flow, and up to date safety processes.
Effective facility management strengthens security, safety, compliance, and operational reliability, creating a foundation that enables healthcare providers to focus on patient care.
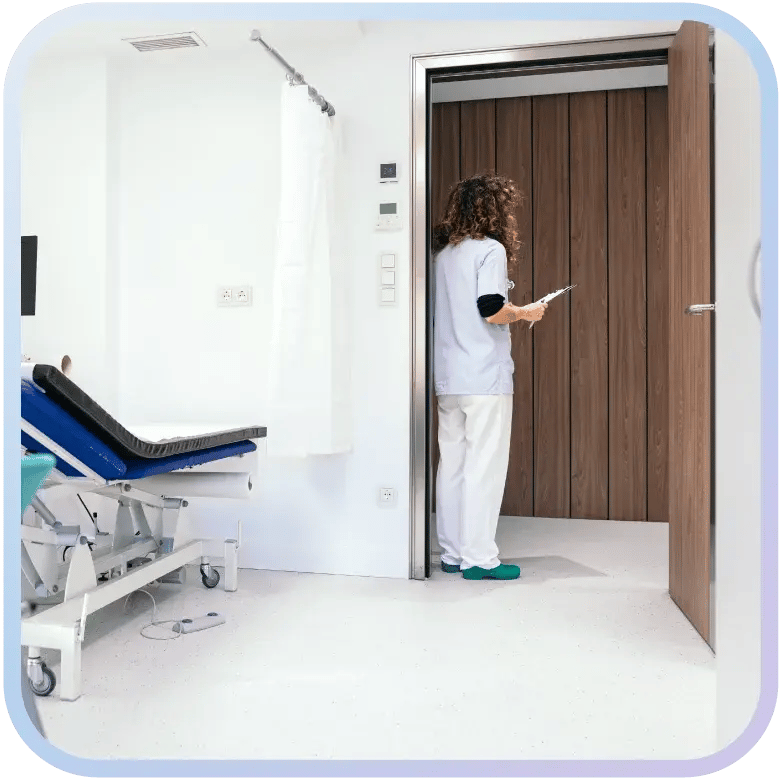

Chapter 2
Why Facility Management Matters in Healthcare
Facility management matters in healthcare because it directly impacts patient safety, compliance, and the delivery of uninterrupted care. Hospitals, clinics, labs, and long-term care centers cannot function effectively if their facilities are not well managed.
How Does Facility Management Protect Care Continuity?
Unplanned downtime in healthcare can delay treatments, cancel surgeries, and jeopardize patient outcomes. Strong facility management reduces the risk by:
These measures keep critical systems running, protect clinical schedules, and ensure patients receive uninterrupted care.
How Does Facility Management Reduce Risks in Healthcare?
Without effective oversight, healthcare facilities are exposed to major risks:
Compliance violations that lead to fines, failed Joint Commission inspections, or loss of accreditation.
Safety incidents that put patients, staff, contractors, and visitors at risk.
Infection outbreaks caused by poor visitor or contractor screening.
Reputational damage that erodes patient trust and community confidence.
The impact varies across settings. In hospitals, failed inspections can halt admissions or elective procedures. In long-term care, poor emergency preparedness can put vulnerable populations at risk. In labs, missing biosafety controls can result in regulatory shutdowns
How Does Facility Management Safeguard Compliance & Institutional Reputation?
Healthcare facilities must prove compliance daily, not only during audits. Facility management supports this by embedding controls into routine operations, such as visitor logs, contractor records, and documented emergency drills.
For hospitals, that means showing OSHA and Joint Commission readiness. For labs, it ensures NIH biosafety standards are followed. For blood banks, it demonstrates FDA compliance for storage and chain-of-custody. By standardizing procedures and documenting activity, facilities reduce risk, protect staff and patients, and strengthen the trust that healthcare providers depend on.
Healthcare facilities face risks that span infection control, patient safety, compliance, and operational continuity. The following areas represent the foundation of effective facility management across hospitals, clinics, labs, long-term care centers, and blood and organ banks.
The core areas of facility management in healthcare are:
- Visitor Management
- Contractor Compliance Management
- Emergency Preparedness
- Asset & Logistics Management
- Identity & Access Management
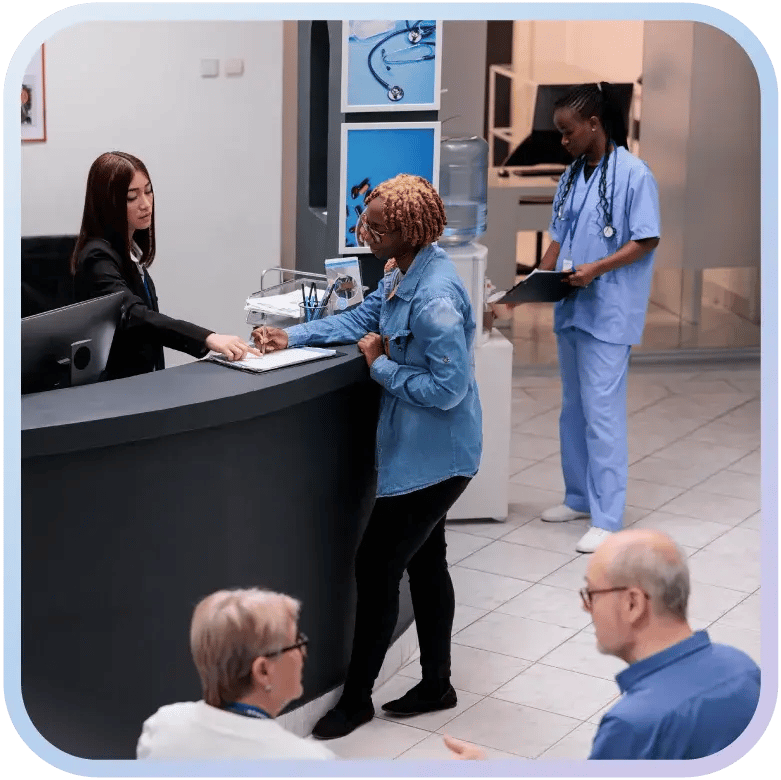

Chapter 3
Why Do Healthcare Facilities Need Visitor Management?
Healthcare facilities need visitor management as part of facility operations because every person entering a hospital, clinic, or lab can affect patient safety, infection control, and regulatory compliance. Unlike typical office settings, care environments include restricted clinical zones, sensitive departments, and specialized equipment where even brief visits must be controlled. By enforcing structured visitor oversight, organizations reduce risks such as infection exposure, unauthorized access, and policy violations tied to hospital standards and accreditation requirements.
How Do Healthcare Facilities Manage Visitor Check-Ins?
Healthcare facilities manage visitor check-ins by recording arrivals, verifying identity, capturing policy or infection-control acknowledgments, issuing badges, and maintaining logs for audits. Methods vary by site, ranging from paper sign-in sheets to spreadsheets, desktop software, and modern cloud-based visitor management systems. Each approach offers different levels of efficiency, accuracy, and compliance support.
Paper sign-in sheets remain common in some facilities. They are inexpensive but introduce errors, are easy to misplace, and do not support audits.
Spreadsheets improve organization but still require manual entry and lack consistency across multiple hospitals, clinics, or campuses.
Standalone software allows faster check-ins and better reporting but often operates in silos without linking to access control, emergency systems, or infection-control workflows.
Cloud-based visitor management systems provide real-time visibility of who is on site, enable pre-registration, and integrate with security and compliance tools.
While older methods can meet basic needs, digital platforms make it easier to scale across multiple locations, reduce administrative work, and provide proof of compliance during inspections or accreditation surveys.
What Are the Core Tasks of Visitor Management in Healthcare?
Every healthcare facility must complete several essential visitor management tasks, regardless of whether they use paper, spreadsheets, or cloud software:
Core visitor management tasks:
- Verifying visitor identity and purpose of entry
- Requiring infection-control or safety acknowledgments before entry
- Issuing badges that restrict access by time and zone
- Recording arrivals and departures accurately
- Maintaining logs for audits and incident investigations
When supported by technology, these tasks extend further:
- Pre-registration and host approvals to shorten lobby times
- Screen against configured watchlists to prevent high-risk entry
- Touchless sign-in to promote hygiene and enhance visitor & patient safety
- Watchlist screening to prevent unauthorized or high-risk entry
- Digital policy attestations, briefings, and safety confirmations captured during sign-in
- Assisted sign-in to support visitors who may have accessibility needs, limited technical fluency, or language barriers.
- Real-time dashboards showing who is on-site across one or many facilities
- Automated sign-out and reporting to ensure records remain current

How Does Visitor Management Support Compliance and Safety?
Strong visitor management is central to meeting both patient-safety obligations and regulatory expectations in healthcare environments. Facilities must ensure anyone entering clinical or restricted areas understands applicable policies, follows infection-control protocols, and avoids zones that require special authorization. Accreditation frameworks and hospital policies emphasize controlled access, clear documentation of who entered sensitive areas, and proof that required acknowledgments were completed.
International standards reinforce these practices by emphasizing hazard identification, emergency preparedness, and accurate, retrievable records. In many care settings, requirements also extend to infection screening or health attestations so visitors do not pose risks to patients or sterile environments.
How Can Healthcare Institutions Set Up Visitor Check-Ins Effectively?
Implementing visitor management requires a structured process that can be applied consistently across sites:
- Define visitor categories (family, vendors, volunteers, auditors) and assign risk levels.
- Require pre-registration and approvals for higher-risk groups.
- Establish site-specific safety acknowledgments or training for regulated zones.
- Configure badge rules for time limits, restricted zones, and escort rules where needed.
- Standardize sign-out and reporting procedures to keep records audit-ready.
This process ensures visitors are screened and managed consistently, while also creating a clear audit trail.
? FAQs for Visitor Management in Healthcare
What counts as a visitor in a healthcare facility?
A visitor is anyone who is not a direct employee, including family members, volunteers, vendors, auditors, and escorted guests.
Do visitors need training or policy acknowledgments?
Yes. Depending on where they will go, visitors must complete required acknowledgments or briefings before entering restricted or high-risk areas.
How long should visitor records be kept?
Follow accreditation standards and internal policy. Retain records long enough to satisfy board reviews, legal obligations, or grant audits.
How does visitor management support emergencies?
Accurate visitor records feed directly into evacuation and mustering systems so that all people on-site, including visitors and contractors, are accounted for.
Why are paper sign-in sheets risky in healthcare?
Paper logs are easy to misplace, difficult to verify, and unreliable during audits, especially where infection control and restricted access are critical.
Why are cloud-based visitor systems preferred?
Cloud-based platforms provide real-time oversight, integrate with access control and safety systems, and create reliable, searchable audit trails across sites.
Explore More Visitor Management Resources
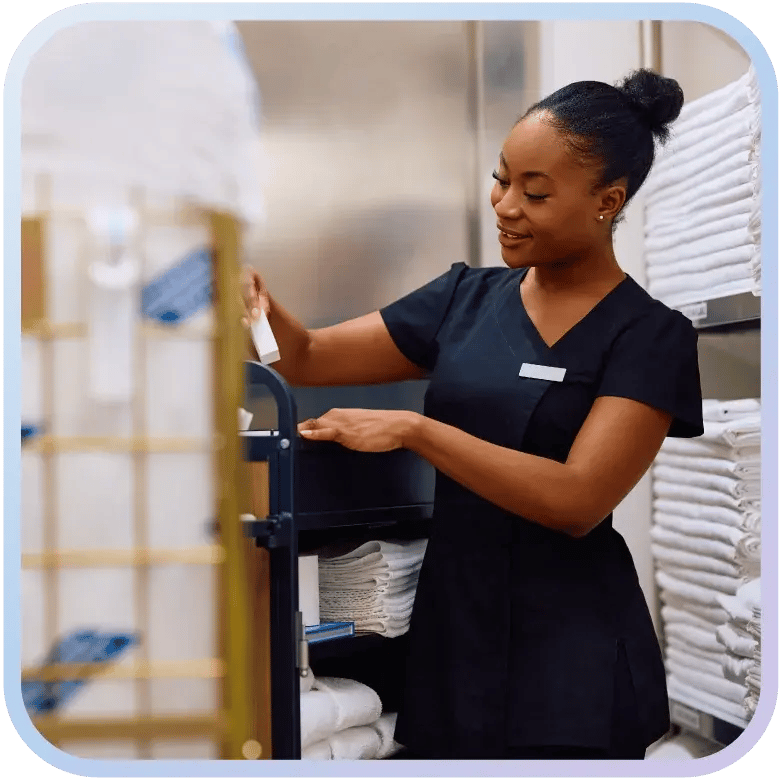

Chapter 4
Why Do Healthcare Facilities Need Contractor Compliance Management?
Healthcare facilities need contractor compliance management to ensure that every vendor, supplier, and contractor entering a site meets safety, infection-control, and insurance requirements before work begins. Contractors often perform specialized or high-risk tasks, from biomedical equipment servicing to HVAC, construction, medical gas work, or waste handling.
If their training, certifications, or insurance are outdated, hospitals can face failed inspections, legal liability, or unplanned downtime that disrupts patient care. Centralizing contractor compliance provides clear proof that standards were enforced across all contractors and vendors.
How Do Healthcare Facilities Manage Contractor Compliance Documentation?
Contractor compliance documentation is managed in several ways, depending on an institution’s resources and maturity of its processes:
Some clinics still rely on binders or file cabinets to store contractor credentials. This approach is prone to lost documents, inconsistent updates, and long retrieval times during audits.
Spreadsheets or Excel, which allows for more organization but requires manual follow-up, is error-prone, and becomes unmanageable across multi-building healthcare campuses.
Standalone software or desktop tools provide more structure for tracking documents, but often lack automation or integration with site check-in systems.
Cloud-based contractor compliance management systems centralize all contractor documents, automate reminders for expiring certifications, and link compliance status directly to site access, ensuring only approved contractors can check-in.
While paper and spreadsheets can capture requirements, they often fail under regulatory pressure. Digital systems scale oversight across locations and provide evidence of compliance in seconds.
What Are the Core Tasks of Contractor Compliance in Healthcare?
Contractor compliance management ensures every outside worker is documented and cleared before entering a site.
Core contractor-compliance tasks:
- Collect, store, and verify licenses, insurance, safety certs, and training.
- Configure approval workflows, flag gaps or expirations, and keep an audit trail.
- Set site-specific requirements by contractor type and risk.
- Track expiration dates with reminders to contractors and facility teams.
- Link compliance status to check-in so only approved contractors access the site.
When supported by technology, these tasks extend further:
- Guided document submission plus review and approvals, with full audit trail.
- Automated expiration tracking with real-time notifications to prevent lapses.
- Central dashboards and cross-site visibility into vendor and contractor status.
- Visitor management system integration to auto-approve at sign-in for fast, authorized check-ins.
- Audit-ready recordkeeping with complete, time-stamped history.

How Does Contractor Compliance Management Support Regulations & Standards?
Contractor compliance management aligns with the governance and accreditation environment of healthcare. Facilities must demonstrate that contractors entering clinical, laboratory, and pharmacy areas have appropriate training, understand site policies, and meet safety and insurance requirements.
Centralized, searchable records provide surveyors and auditors with proof that prerequisites were met before work began and that access was controlled. Digitizing these controls streamlines readiness, reduces manual effort, and ties compliance status to access permissions for consistent enforcement across sites.
How Can Healthcare Facilities Set Up Contractor Compliance Effectively?
A strong contractor compliance program is built on clear requirements and automated enforcement:
- Define contractor categories and risk levels.
- Establish standardized approval workflows with expiration rules and automated reminders.
- Require digital submission of documents and training records to reduce manual tracking.
- Integrate compliance status directly to check-in systems so only compliant contractors gain access.
- Maintain audit-ready reports and exception handling procedures for inspections.
This approach ensures contractors are not just managed at the project level but are consistently vetted and documented across the entire facility.
? FAQs for Contractor Compliance in Healthcare
What documents are typically required from contractors?
Proof of insurance, licenses, safety training or certifications, and any site-specific credentials, all tracked with expiration dates.
How do multi-site hospital systems keep standards consistent?
Centralize baseline requirements in a shared system while allowing each hospital or clinic to add local add-ons for unique risks.
How can contractors clear access faster?
Keep documentation current and pre-approved so check-in is quick with fewer escalations.
How is audit readiness maintained?
Audit readiness is maintained by keeping a digital trail of all documents, approvals, rejections, and expirations, making it easy to export evidence for inspectors.
Why are spreadsheets and paper records risky?
They rely on manual follow-up, are difficult to standardize across sites, and make it challenging to prove compliance during audits.
Why are cloud-based systems preferred for contractor compliance management?
Cloud platforms automate expiration tracking and approvals, provide real-time dashboards, and connect compliance records to site access, making oversight more reliable and scalable across healthcare networks.
Explore More Contractor Compliance Management Resources

Chapter 5
Why Do Healthcare Institutions Need Emergency Management & Preparedness?
Healthcare facilities need strong emergency management and preparedness because healthcare facilities have diverse risks, including chemical spills, severe weather, infectious disease events, and security threats. Sites must account not only for staff but also for patients, contractors, and visitors who may be unfamiliar with procedures. A structured program ensures every person on-site can be alerted, evacuated or sheltered, and accounted for quickly, while producing the documented proof surveyors and regulators require.
How Do Healthcare Facilities Manage Emergencies and Preparedness?
Healthcare facilities manage emergencies by combining defined procedures with tools that improve speed and accountability. Methods vary by facility, ranging from paper rosters and radio calls to spreadsheets, desktop software, and modern cloud-based emergency management systems. Each approach offers different levels of accuracy, visibility, and compliance support.
Paper rosters & radio check-ins remain common in some facilities. They are inexpensive but slow, error prone, and hard to audit.
Spreadsheets improve organization but still require manual data entry and lack consistency across multiple sites.
Standalone software speeds alerts and musters but often operates in silos without linking to access control or visitor systems.
Cloud-based emergency systems provide centralized oversight, real-time evacuation tracking, mass notifications, and integration with security and compliance tools.
While older methods can meet basic needs, digital platforms make it easier to scale across clinics and hospitals, reduce response times, and provide proof of compliance during inspections.
What Are the Core Tasks of Emergency Management in healthcare?
At a minimum, healthcare facilities must plan for emergencies, document drills, and account for every person on-site.
Core emergency preparedness tasks:
- Defining emergency roles and responsibilities for supervisors, floor leaders, and safety officers
- Mapping muster points and building sweep routes across campus
- Scheduling and documenting drills to meet regulatory requirements
- Capturing attendance, headcounts, response times, and all-clear confirmations
- Reviewing drill and incident performance to identify gaps and corrective actions
When supported by technology, these tasks extend further:
- Automated mass notifications with two-way messaging via SMS, email, or calls
- Real-time digital musters and roll calls across multiple muster points
- Live dashboards showing who is on premise across one or many buildings
- Reconciliation of headcounts with access control and sign-in data
- Exportable drill and incident reports to ensure records remain current
- Building sweeps that divide the facility into zones, ensuring systematic and focused safety checks for an organized and efficient evacuation process.

How Does Emergency Management Support Compliance & Safety?
Emergency management supports compliance by demonstrating that healthcare organizations can protect patients and staff and maintain continuity of care during incidents.
Facilities need documented emergency action procedures, tested evacuation workflows, and accurate records that show everyone on-site was included and accounted for.
Digital platforms help maintain OSHA-aligned records and support programs modeled on international standards such as ISO 45001 by logging drills, timing, and outcomes for continuous improvement.
How Can Healthcare Facilities Set Up Emergency Preparedness Effectively?
Building an effective program requires both planning and practice:
- Define emergency scenarios specific to each campus and document clear procedures.
- Assign roles and responsibilities for administrators, faculty, staff, and student leaders.
- Communicate muster points and establish digital roll call processes.
- Schedule and document drills that align with state and federal requirements.
- Review trends across sites and refine procedures to close gaps and strengthen future preparedness.
This approach ensures that emergency preparedness is not a one-time exercise but a continuous, auditable process.
? FAQs for Emergency Management in Healthcare
How do healthcare facilities account for visitors and contractors during an evacuation?
Integrate visitor and contractor records with the emergency system so they receive alerts and appear in live roll calls and mustering lists.
What records should be kept for audits or surveys?
Maintain digital evacuation logs, drill reports, attendance data, incident duration, and time-to-clear metrics, organized by site and scenario.
How often should drills be conducted?
Follow organizational policy and applicable safety requirements. Each drill should be documented and reviewed for improvements.
Can emergency procedures vary by scenario?
Yes. Configure workflows, roles, and messages for fires, medical events, severe weather, chemical spills, or security incidents.
Why are manual roll calls risky in healthcare?
Paper lists and manual headcounts are often incomplete or inaccurate during large movements of people, making compliance harder to prove. Digital systems improve speed and accuracy.
Why are digital systems becoming the standard?
They accelerate accountability, reduce human error, and provide exportable, audit-ready records that support both internal reviews and regulatory inspections.
Explore More Emergency Management Resources

Chapter 6
Why Do Healthcare Institutions Need Asset and Logistics Management?
Healthcare facilities need asset and logistics tracking to control how medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, devices, and mail move through hospitals and clinics every day. From central receiving to point of care, every handoff introduces risk of delay, loss, or improper handling that can impact patient care.
Poor oversight leads to shortages, expired products in circulation, and audit findings, while weak flow at docks and storerooms creates bottlenecks. Standardizing processes for tracking and internal distribution ensures the right items reach the right location at the right time, with a clear chain of custody for audits and investigations.
How Do Healthcare Organizations Manage Assets and Logistics?
Healthcare organizations use a mix of manual and digital methods that vary by site maturity:
Paper logs and clipboards are still common for recording tool check-outs or deliveries, but prone to errors, loss, and illegible handwriting.
Spreadsheets offer better organization but require manual updates, which become unreliable as networks scale.
Legacy point solutions provide digital tracking for specific workflows like mailrooms but often operate in isolation from other systems.
Cloud-based asset and logistics systems data across receiving, storage, usage, and outbound. These systems integrate with ERP and pharmacy tools, and use barcodes, to track location, condition, and movement in real time with audit-ready trails.
Facilities that rely on manual processes often struggle during audits and recalls, while those using integrated digital tools gain real-time visibility and standardized reporting across multiple locations.
What Are the Core Tasks of Asset and Package Tracking in Healthcare?
Effective management spans the entire lifecycle of items.
Core asset & logistics tasks:
- Receiving inbound items, scheduling docks, and checking in drivers
- Tracking lots and batches to maintain chain of custody through use or shipment
- Controlling storage zones and restricted areas for regulated or high-value items
- Managing tools and equipment with check-in/out workflows
- Monitoring conditions for sensitive materials, preparing shipments with accurate labeling, and capturing exceptions
When supported by technology, these tasks extend further:
- Central receiving with purchase order line-item receiving to verify and close POs in one screen.
- Real-time visibility and chain-of-custody tracking for each item across sites.
- Digital proof of delivery using signatures and photo verification.
- Real-time notifications and alerts to recipients and teams.
- Integrations with ERP platforms and intelligent lockers to streamline handoffs and records.

How Does Asset and Package Tracking Support Compliance?
Asset and logistics oversight supports compliance by showing how drugs, devices, and supplies were received, stored, handled, and delivered. Traceability and secure chain of custody help meet requirements such as FDA for pharmaceutical tracking and Joint Commission expectations around equipment availability and reliable processes.
Digital platforms provide real-time logs, temperature history for perishables, and searchable records for audits and recalls.
How Can Healthcare Logistics Set Up Asset and Package Tracking Effectively?
A structured program ensures resources move through campuses securely and efficiently:
- Define item categories (pharmaceuticals, devices, supplies, loaners) and assign ownership rules.
- Map storage zones and movement paths, and track transfers with digital proof of movement.
- Standardize receiving, movement, and check-in/out with barcode-based workflows, notifications, and purchase-order line-item receiving.
- Implement traceability with barcode scanning and PO linkage to maintain chain of custody from intake to delivery.
- Connect to your ERP, lockers, and other logistics systems, then use real-time dashboards and alerts for centralized reporting and exceptions; add temperature monitoring where required.
This approach reduces losses, improves utilization, and provides clear documentation for audits.
? FAQs for Asset and Logistics Management in Healthcare
What is the difference between assets and inventory?
Assets are durable items like medical devices and IT equipment. Inventory refers to consumables and pharmaceuticals that move through care delivery.
How does chain-of-custody tracking work?
Each item receives a unique identifier that follows it through every handoff, ensuring full traceability for audits and investigations.
Do hospitals need mobile scanning?
Yes. Barcode scanning improves accuracy, speeds up receiving and check-out, and ensures movements are logged in real-time.
Why are paper logs risky for healthcare?
They are error-prone, time-consuming to search, and unreliable when auditors or boards require accurate, complete records.
Why are cloud-based logistics platforms preferred?
They integrate with campus systems, provide real-time visibility, and generate reliable, searchable records across multiple buildings.
How do facilities manage shared or loaner equipment?
Check-in/out workflows with due dates, condition notes, and reminders reduce loss, downtime, and maintenance issues.

Chapter 7
Why Do Healthcare Facilities Need Identity & Access Management?
Healthcare facilities benefit from identity and access management as it extends security and access control to protect patients, staff, medications, and clinical equipment by ensuring only the right people can enter specific areas at the right time. Hospitals and clinics include restricted spaces such as pharmacies, ICUs, operating rooms, research labs, and data rooms where access must be tightly controlled.
Without strong identity and access controls, unauthorized entry can lead to safety incidents, privacy breaches, drug diversion, or regulatory findings. A structured access program also produces the documentation surveyors expect, proving that permissions are properly reviewed and enforced.
How Do Healthcare Institutions Manage Identity and Access?
Identity and access management in healthcare is handled through a mix of manual and digital systems that vary by institution size and complexity:
Manual sign-in and key distribution is still used in smaller sites, but risky due to lost keys, lack of tracking, and no audit trail.
Standalone badge systems provide basic access controls, but often lack integration with HR systems or visitor check-ins.
On-premise PIAM solutions assign permissions more systematically, but can be difficult to scale across multiple sites.
Cloud-based identity and access management systems automate provisioning, enforce role- and zone-based permissions, making compliance and oversight easier.
While manual and legacy systems can cover basic needs, digital platforms provide centralized control, ensure least-privilege access, and simplify audits.
What Are the Core Tasks of PIAM in Healthcare?
Most healthcare facilities and clinics need to complete several essential identity and access tasks, regardless of whether they use paper logs, spreadsheets, or cloud software:
Core identity and access management tasks:
- Verify identities and pre-approve employees, contractors, and visitors.
- Assign role- and zone-based permissions aligned to risk.
- Issue and manage temporary credentials with time and area limits.
- Monitor access activity and maintain audit records.
- Review permissions periodically and revoke access when it’s no longer appropriate.
When supported by technology integrated with visitor management, these tasks extend further:
- Automate credential issuance and permission provisioning with rule-based workflows, tied to visitor management checks like approvals and watchlists.
- Set precise time-bound and area-specific access levels, with credentials that can auto-expire on sign-out or after a set duration.
- Issue digital credentials as QR codes at the kiosk and by email so guests can access gates without badge printers.
- Integrate with access control systems and use real-time reporting and centralized administration to see who accessed what, when, across sites.
- Automated sign-out and reporting to ensure records remain current.

How Does Access Management Support Compliance and Safety?
Identity and access management is central to compliance because hospitals must prove not only who entered a facility, but also why they were allowed in and under what conditions.
Access controls help enforce prerequisites for high-risk areas, safeguard drug storage and PHI, and limit restricted spaces to trained, authorized personnel. Maintaining accurate, retrievable access logs and approvals supports accreditation surveys and internal audits, while aligning with broader safety and security programs.
How Can Clinics & Hospitals Set Up PIAM Effectively?
Setting up an effective access management program requires both policy and technology:
- Define access profiles with specific areas, times, and durations, then use rule-based workflows to automate who gets which permissions.
- Tie credential issuance to visitor management checks so approvals and watchlists must pass before access is granted.
- Choose credential types and expirations that fit the scenario, including digital QR credentials issued from the kiosk or by email, with options to expire on sign-out or after a set time.
- Integrate with your access control system to apply permissions at doors, turnstiles, gates, and more, while keeping everything centrally managed.
- Use real-time reporting and audit logs to review who accessed which points, when, and to support periodic access reviews and revocations.
This approach prevents access creep, tightens security at sensitive zones, and leaves a clear, audit-ready record of how access decisions were made.
? FAQs for PIAM in Healthcare
What is PIAM in a healthcare context?
PIAM (physical identity and access management) is a system that manages identities, credentials, and permissions across sites, applying role- and zone-based rules for clinical and administrative areas.
How do hospitals handle temporary workers, students, or auditors?
They are issued time-bound, zone-restricted badges tied to verified prerequisites and, when needed, escort requirements.
How long should access logs be retained?
Retention should follow healthcare policy and regulatory expectations, with logs accessible for audits and investigations.
How do institutions reduce access violations?
Apply least-privilege permissions, conduct proactive reviews, and use real-time monitoring with alerts for unauthorized activity.
Why are manual systems risky for access control?
Manual logs or physical keys lack reliable records, are prone to misuse, and make compliance difficult to prove during audits.
Why are cloud-based access systems increasingly preferred?
They simplify provisioning, enforce consistent policies across multiple sites, integrate with HR and visitor systems, and provide searchable audit trails that support accreditation and security requirements.

Chapter 8
Compliance and the Regulatory Landscape
Facility management supports compliance in healthcare by embedding safety, security, and operational controls into daily workflows. Facilities must not only meet federal, state, and accreditation standards but also prove compliance through audit-ready documentation.
Hospitals & Clinics
Main Focus: Infection control, visitor/contractor oversight, emergency preparedness, audit documentation.
|
United States |
Canada |
Global |
|
Joint Commission (JCAHO); CMS – Medicare/Medicaid Conditions of Participation; HIPAA – patient data protection; OSHA – workplace safety |
Health Canada; CSA – healthcare safety standards; provincial health regulations
|
WHO – International Patient Safety Goals; ISO 45001 – occupational safety standards |
Long-Term & Home Care
Main Focus: Resident safety, fall prevention, secure access, evacuation planning.
|
United States |
Canada |
Global |
|
CMS – Long-Term Care regulations; |
Health Canada; provincial ministries of health; CSA – elder care safety standards |
WHO – long-term care and elder safety guidelines
|
Healthcare Research Institutions
Main Focus: Lab access control, biosafety compliance, sample chain-of-custody
|
United States |
Canada |
Global |
|
NIH – biosafety standards; HIPAA – data security; OSHA – lab safety |
Health Canada; CCOHS – biosafety and workplace safety |
ISO 15190 – medical lab safety; WHO biosafety guidance |
Medical Laboratories & Imaging Centers
Main Focus: Sample handling, equipment calibration, access logs
|
United States |
Canada |
Global |
|
CLIA – Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments; OSHA – lab worker safety |
Health Canada; provincial health lab licensing |
ISO 15189 – medical laboratory quality; ISO 13485 – equipment management
|
Blood & Organ Banks
Main Focus: Refrigeration monitoring, chain-of-custody, secure access
|
United States |
Canada |
Global |
|
FDA – blood and tissue storage compliance; OSHA – staff safety |
Health Canada; Canadian Blood Services; CSA – blood storage standards |
WHO – global blood safety program; ISBT 128 – traceability standards
|

Why Is Compliance Tied to Facility Management?
Facility management helps healthcare facilities stay audit ready by embedding compliance into daily operations such as visitor oversight, contractor validation, asset tracking, and emergency preparedness. These activities create documented proof that regulators and accrediting bodies require.
When compliance is part of routine processes, audits become faster and less disruptive. Strong facility management turns regulatory expectations into structured practices that keep hospitals, clinics, labs, and care centers prepared year-round, protect patient safety, and maintain trust in the quality of care.

Chapter 9
Technology & Digital Transformation in Facility Management
Facility management software in healthcare makes core processes easier to manage, more accurate, and consistently audit ready. By replacing paper logs, spreadsheets, and manual communication with connected systems, facilities improve oversight of visitors, contractors, emergencies, assets, and access across hospitals, clinics, labs, and long-term care centers
How Is Facility Management Shifting from Manual to Digital?
Healthcare facility management is moving from paper to software by replacing sign-in sheets, binder-based safety records, and manual roll calls with digital tools that centralize records and standardize compliance. Manual processes are time consuming, error-prone, and difficult to maintain across multiple facilities.
With software, hospitals and care centers can automate updates, maintain reliable audit trails, and respond faster during inspections or emergencies. This shift allows facility leaders to move from reactive oversight to proactive management that supports patient safety and compliance.
What Are the Benefits of Facility Management Software?
The benefits of facility management software in healthcare include reducing manual work, improving compliance, and strengthening visibility across every site. By embedding software into daily operations, facilities can maintain safer environments and stay inspection ready year-round.
Automated Compliance Workflows
Verifying contractor credentials, tracking visitor screenings, and recording emergency drills without manual paperwork.
Analytics for Improvement Support
Using reports on incidents, drills, and inspections to identify risks and close gaps before they become compliance failures.
Connected Systems
Connecting access control, HR/workforce management, safety, and compliance systems to reduce duplication and provide a clear view of activity across all sites.
Audit-Ready Records
Maintaining secure logs that demonstrate compliance with Joint Commission, CMS, OSHA, and FDA requirements.
Real-Time Visibility
Knowing who is on-site, where critical assets are located, and how staff respond during emergencies.
Why Does Facility Management Software Matter for Healthcare?
Facility management software works behind the scenes to make healthcare facilities safer, more compliant, and more efficient. By turning routine oversight into structured workflows, it helps hospitals, clinics, labs, and care centers stay prepared, protect patients, and reduce operational risk.
One platform that addresses these needs is FacilityOS, which offers modular solutions for visitor management (VisitorOS), emergency and evacuation management (EmergencyOS), contractor compliance (ContractorOS), asset and logistics management (LogisticsOS), and physical identity and access management (SecurityOS). Healthcare institutions can start with one module and expand as their needs evolve, ensuring scalability across single campuses or entire districts while maintaining a unified user experience and centralized reporting.
Explore More Technology Resources

Chapter 10
Measuring Success: KPIs for Facility Management
Measuring results shows whether healthcare facility programs are working. In healthcare, that means focusing on safety, compliance, and continuity of care. Clear, well-defined KPIs help hospitals, clinics, and long-term care sites monitor progress, find gaps, and stay ready for audits and inspections.
What Are Key KPIs in Facility Management for Healthcare?
Because every organization is different, do not copy a generic list. Design KPIs that fit your risk profile and workflows. Use this approach:
Define Outcomes & Requirements
Identify key results (fewer incidents, faster evacuations, audit readiness) and link them to applicable regulations like FDA and Joint Commission.
Map Workflows
Connect outcomes to the processes that drive them: visitor check-in, contractor credentialing, emergency drills, access control, and logistics tracking.
Select Metrics
Choose leading indicators (% visitors pre-registered, % drills completed on time) and lagging indicators (evacuation times, access violations) that you can capture automatically.
Set Definitions & Targets
Write clear definitions, assign owners, establish thresholds, and set goals by building, department, or campus type.
Pilot and Refine.
Test metrics at one site, confirm they respond to process improvements, and retire any that don't drive action.
Standardize & Improve
Roll out common metrics across locations, review regularly in safety committees, and assign corrective actions to demonstrate continuous improvement.
Quick test: A KPI is useful if a charge nurse or facilities lead can explain how to improve it today and the data is available in real-time.
Why Are KPIs Important in Facility Management?
KPIs replace assumptions with evidence. They show whether safety and security controls work as intended, whether preventive maintenance is protecting critical systems, and whether training and access reviews keep pace with staffing and vendor changes. Clear measures help teams prioritize fixes, document progress for regulators and accreditors, and maintain consistency across campuses and units.
How Do KPIs Show ROI in Facility Management?
Well-chosen KPIs connect everyday improvements to outcomes leadership values. Fewer safety events reduce liability and rework. Strong survey performance shortens audits and lowers the risk of findings that disrupt operations. Better visibility prevents product loss from cold-chain failures and reduces overtime tied to unplanned outages. Together, these results show that disciplined, data-driven facility management protects patient safety, compliance, operational reliability, and trust.

Chapter 11
Future of Facility Management in Healthcare
Healthcare facilities are beginning to use data and connected systems to strengthen safety, compliance, and efficiency. The future of facility management will be shaped by continuous compliance practices, smarter use of data, integrated systems, sustainability initiatives, stronger cybersecurity, and better support for staff. These advancements give hospitals, clinics, labs, and long-term care centers real-time visibility while keeping them audit ready.
How Will Facility Management Evolve in Healthcare?
The future of healthcare facility management will focus on several interconnected areas:
- Continuous compliance: Facilities will move beyond preparing only when an audit is scheduled. With software, organizations can monitor risks daily, track expired certifications, and document emergency drills so they remain audit ready at all times. This reduces risk, saves staff time, and ensures patient care continues without disruption.
- AI and data-driven insights: Artificial intelligence will help analyze safety and compliance data to flag infection risks, suggest ways to improve patient flow, and identify inefficiencies in resource use. By turning raw data into actionable insights, AI will make it easier to prevent risks before they escalate.
- System integration: Hospitals and clinics will increasingly connect safety, security, logistics, and compliance systems. Integration reduces errors, shortens response times, and provides leadership with a clear view of on-site activity. It also creates the foundation for AI tools to deliver accurate recommendations.
- Sustainability and resilience: Energy efficiency and climate preparedness will become central to facility management. Hospitals and labs will prioritize reducing energy waste, lowering emissions, and ensuring reliable backup power during extreme weather events. These measures support both regulatory compliance and patient safety.
- Cybersecurity and data protection: As facilities rely on connected systems, protecting sensitive patient data will be critical. Future practices will need to comply with HIPAA and NIST standards to safeguard visitor logs, access records, and contractor databases against cyber threats.
- Supporting healthcare staff: With ongoing workforce shortages, facility management will help reduce administrative burden. Automating visitor oversight, contractor verification, and emergency drills allows clinical staff to focus more on patient care instead of paperwork.
- Adapting to evolving regulations: Regulatory requirements from The Joint Commission, CMS, OSHA, and NIH are becoming more demanding. Facility management will continue to align daily operations with these evolving standards to maintain compliance and avoid disruptions to patient care.
Taken together, these trends show that the future of facility management in healthcare is about being proactive rather than reactive. By embedding compliance and safety into daily routines, facilities can reduce risk, protect patients, and build resilience for the challenges ahead.
Conclusion
Closing Thoughts on Facility Management in Healthcare
Healthcare facilities operate in environments where patient safety, compliance, and operational reliability cannot be compromised. Facility management provides the framework that keeps people safe, protects critical resources, and ensures continuity of care.
Strong processes supported with facility management software reduce risks, improve visibility, and simplify compliance. They make audits less disruptive, keep training and safety procedures consistent, and ensure access to restricted areas is properly controlled.
When healthcare facilities prioritize structured and well-documented management practices, they achieve more than regulatory compliance. They strengthen resilience, safeguard patients and staff, and build trust with regulators and the communities they serve. Facilities that take this approach are better prepared to deliver safe, reliable care in an increasingly complex and highly regulated healthcare landscape.
? FAQs About Facility Management in Healthcare
How should a hospital get started with facility management software?
Start with a single-site or single-unit pilot. Define owners, import core people and place data, connect priority integrations (directory, access control), and run one full cycle for visitors, contractors, emergencies, and assets. Use results to standardize templates, then roll out by campus or region with a clear governance model and training plan.
How does facility management software protect patient data and HIPAA privacy?
These tools primarily store operational data, not clinical records. Enforce SSO, role-based access, and audit logs; limit user permissions by role and location; encrypt data in transit and at rest; and apply retention policies for visitor, contractor, and access logs aligned to HIPAA and internal policy.
How do multi-site health systems keep policies consistent while allowing local differences?
Create system-wide standards and templates for visitor rules, contractor documents, emergency profiles, and access roles. Allow site-level add-ons for local risks, while central reporting monitors exceptions, expirations, and drill performance across all facilities.


