Industry Guide
Corporate Facilities Management
.webp?width=960&height=646&name=Corporate-Pillar-Hero-pip%20(1).webp)
Facility management in corporate & commercial environments is the art of running people-centric, brand-forward spaces at portfolio scale. Teams juggle multi-site, often multi-tenant buildings while keeping lobbies flowing, coordinating security and access control with IT, and managing a constant mix of guests, contractors, and deliveries.
Corporate operations rely on constant coordination between staff, visitors, vendors, and emergency teams. Yet most facilities still manage these movements with paper logs, spreadsheets, and manual calls. Modern facility management now depends on connected, digital processes that protect compliance and safety while reducing administrative work.
For corporate environments, sites prize a polished front door experience, reliability in their services, and a measurable impact on revenue/costs.
Summary
Facility management in corporate and commercial environments keeps sites safe, compliant, and consistent with brand standards. It protects employees, tenants, guests, and sensitive areas while reducing operational risk and inspection findings. By focusing on visitor oversight, contractor compliance, emergency preparedness, asset and logistics management, and identity and access control, leaders improve continuity and trust across locations.
Why Facility Management Matters in Corporate & Commercial:
-
Meets building, fire, life-safety, and privacy expectations with documented proof.
-
Protects people, property, and information in mixed public and restricted spaces.
-
Minimizes service disruption across offices, branches, stores, hotels, venues, and shared buildings.
-
Strengthens brand reputation through consistent lobby, back-of-house, and emergency experiences.
Core areas of focus: Visitor management, contractor compliance, emergency preparedness, asset and logistics management, and identity and access control.
Compliance connection: Facility operations embed requirements into daily workflows, creating audit-ready records for inspections, landlords, clients, and insurers.
Measuring success: Track KPIs such as visitor check-in time, contractor pre-clear rate, evacuation time and percent accounted for, denied access attempts, package trace time, asset utilization, and audit finding closure time.

Chapter 1
What Is Facility Management in Corporate & Commercial?
Facility management in corporate and commercial settings is the day-to-day orchestration of people, spaces, and safety that keeps offices, retail stores, venues, hotels, and multi-tenant properties running smoothly. It covers how visitors, employees, vendors, and deliveries enter and move through a site, how sensitive areas stay protected, how incidents are handled, and how the experience remains consistent with the brand.
In practice, that means tightly managed check-ins, contractor controls, identity and access across zones, environmental and occupancy monitoring, and clear playbooks for emergencies. The goal is a workplace and guest experience that is safe, compliant, on-brand, and resilient, supported by audit-ready records and real-time visibility into who is on-site.
How Does Facility Management Differ Across Corporate Sectors?
It differs by sector because the people you host, the spaces you secure, and the regulations you answer to are not the same, so controls and workflows must adapt accordingly. Here is how that plays out:
Technology & Software
Executive suites, engineering labs, and server rooms require strict role-based access and NDA or policy acknowledgments at check-in. Teams balance productivity with protection of IP and systems, maintaining precise logs and rapid clearance procedures for restricted areas.
Banking & Financial Services
Branches, operations centers, and trading floors emphasize controlled access to vaults and records rooms, detailed visitor identity verification, and after-hours approvals. Facilities also coordinate frequent vendor visits and scheduled maintenance without disrupting customer service.
Retail, Hospitality & Consumer Brands
Front-of-house safety and experience must align with back-of-house controls for stockrooms, cash handling, kitchens, and loading docks. Facilities manage high-traffic peaks, vendor and merchandiser access, and delivery flow while keeping stores audit-ready and evacuation routes clear.
Real Estate & Property Management
Owners and operators oversee lobby security, dock schedules, permits, and life-safety standards across different tenants. Consistent contractor compliance, hot-work controls, and shared muster procedures reduce risk and minimize disruption to occupants.
Media & Entertainment
Studios, stages, and venues coordinate talent, crew, and audience access on tight timelines. Credentialed zones such as control rooms and production areas need strict badge rules, while crowd management and accurate headcounts keep events safe and on schedule.
What Are the Main Goals of Facility Management in Corporate & Commercial?
The main goals are to protect people, protect the brand and experience, ensure compliance and accountability, and maintain uptime and continuity across every location. These priorities guide daily decisions and shape how teams design procedures, staff lobbies, and plan for incidents.
Protect People
Provide a safe environment for employees, guests, vendors, and contractors. Standardize briefings and acknowledgments, and ensure everyone understands building procedures and emergency actions.
Ensure Compliance & Accountability
Meet regulatory and policy requirements, from access and visitor logs to permits and drills. Keep searchable, audit-ready records that document who was on-site, where they went, and what was approved.
Protect Brand & Experience
Deliver spaces that are welcoming, reliable, and easy to navigate. Smooth check-ins, clear signage, and well-run service areas uphold trust with customers, tenants, and staff.
Maintain Uptime & Continuity
Prevent avoidable disruptions through coordinated vendor access, planned maintenance windows, strong emergency preparedness, and real-time roster visibility. Consistent operations protect revenue and reputation across sites.
Together, these priorities create workplaces and public spaces that feel safe and professional, operate without surprises, and strengthen the brand over time.

Chapter 2
Why Facility Management Matters in Corporate & Commercial Industries
Facility management matters because it keeps workplaces, stores, venues, and multi-tenant properties safe, open for business, and aligned with brand expectations while meeting regulatory and policy obligations. A single miss — an unvetted contractor, an unclear evacuation route, or a door left propped open — can lead to service disruption, failed inspections, or reputational harm. Effective facility oversight keeps locations audit-ready, consistent across sites, and prepared for emergencies without slowing day-to-day operations.
How Does Facility Management Protect Business Continuity?
It protects continuity by preventing small operational lapses from turning into closures or service delays.
These practices reduce interruptions, keep customer-facing areas open, and protect revenue across offices, branches, stores, and venues.
How Does Facility Management Reduce Business Risks?
It reduces risk by closing common gaps that create safety, compliance, or security events.
Policy or code violations that lead to fines, failed inspections, or insurance issues.
Safety incidents affecting employees, guests, contractors, or crowds.
Loss or exposure of sensitive assets and information due to weak access controls.
Reputational damage when service is disrupted or visitor experiences fall short.
Impact varies by sector. In banking, weak lobby and vault controls jeopardize audit outcomes. In retail and hospitality, poor back-of-house oversight or blocked egress routes can trigger citations and closures. In media and entertainment, credential errors or inaccurate headcounts can halt a production or delay a live event. In multi-tenant buildings, lax contractor management can disrupt multiple occupants at once.
How Does Facility Management Safeguard Compliance & Brand Reputation?
Facility management safeguards compliance and brand reputation by building clear rules into daily operations and documenting that they were followed.
Facility teams maintain searchable access and visitor logs, document contractor approvals and permits, and keep drill records and life-safety checks current. In financial services, that means strict badge rules for records rooms and documented escort policies for vendors. In technology and software, it means protecting hardware labs and data rooms with role- and time-bound access and signed acknowledgments. In hospitality and retail, it means demonstrating adherence to fire and life-safety requirements, kitchen and stockroom controls, and clear evacuation routes. By standardizing procedures and capturing evidence as work happens, organizations reduce risk, protect people, and uphold the brand experience customers and tenants expect.
Corporate and commercial properties face a mix of safety, compliance, and experience risks that vary by setting—offices, branches, stores, hotels, venues, and multi‑tenant buildings. The foundation of an effective program rests on a small set of disciplines that work together across locations and teams.
- Visitor Management
- Contractor Compliance Management
- Emergency Preparedness
- Asset & Logistics Management
- Identity & Access Management

Chapter 3
Why Do Corporate & Commercial Businesses Need Visitor Management?
Corporate and commercial businesses need visitor management because every non-employee who enters—whether to an office, branch, store, venue, or shared building—affects safety, privacy, security, and brand experience. Unlike closed production floors, corporate environments mix public spaces with restricted zones: records rooms, cash-handling areas, executive suites, data or server rooms. Even a short visit to these areas must be controlled. Structured oversight reduces risks including data exposure, theft, tailgating, blocked egress, and regulatory findings tied to OSHA and fire/life-safety codes. In certain sectors, it also addresses privacy and financial controls (GDPR/CCPA, PCI DSS, GLBA/FFIEC) or security certifications (SOC 2/ISO 27001). Proper visitor management keeps locations open for business, audit-ready, and aligned with brand standards.
How Do Corporate Businesses Manage Visitor Check-Ins?
Corporate and commercial facilities manage check‑ins by verifying visitor identity, capturing required acknowledgments, issuing time‑bound badges, and maintaining accurate logs. Organizations typically use one of four approaches—each with distinct trade‑offs for security, compliance, and scalability:
Paper sign-in sheets are common at small corporate sites, but vulnerable to transcription errors, privacy exposure at reception desks, and limited reporting capabilities for compliance audits or incident investigations.
Spreadsheets provide basic organization for visitor tracking, yet still require manual data entry and often use inconsistent formats across multiple corporate locations; challenging to consolidate during enterprise‑wide compliance reviews.
Standalone software accelerates check‑in processing and generates cleaner digital logs, but typically operates independently without integration to access control systems, watchlists, HRIS platforms, or life‑safety tools.
Cloud-based visitor management systems provide real-time visibility of who is on site, enable pre-registration for events, and integrate with security and compliance tools.
While any method can record visitor names and arrival times, the critical difference lies in how reliably the system enforces corporate security policies, scales across enterprise portfolios, and produces compliant documentation when regulators, insurance carriers, or commercial clients request verification.
What Are the Core Tasks of Visitor Management in Corporate & Commercial?
Visitor management in corporate and commercial facilities involves several key operational tasks that ensure secure, compliant, and efficient access control:
Core visitor management tasks:
- Verify visitor identity and purpose of visit.
- Present and capture acknowledgments for safety, security, and conduct policies.
- Issue time-bound, zone-restricted badges with escort requirements.
- Record accurate visitor arrivals and departures.
- Maintain searchable, audit-ready visitor logs for compliance investigations.
When supported by technology, these tasks extend further:
- Pre-registration workflows and host approvals to reduce lobby wait times.
- Automated watchlist screening with rule-based visitor denials and escalations.
- Digital signature capture for NDAs, privacy notices, and security briefings at check-in.
- Real-time on-site dashboards displaying visitor location by floor, tenant, or zone.
- Automated sign-out reminders, badge return tracking, and scheduled compliance reports.
- Integrated features including visitor Wi-Fi provisioning, meeting room check-in, and temporary parking pass management tied to visitor records.
- Real-time dashboards showing who is on-site across one or many facilities.
- Automated sign-out and reporting to ensure records remain current.

How Does Visitor Management Support Compliance and Safety?
Visitor management supports compliance, safety, and privacy by building controls into everyday operations and creating records you can verify later.
- Safety compliance means briefings are delivered, PPE and escort rules are enforced, headcounts stay accurate for evacuations, and exit paths remain clear.
- Access control is maintained with time-bound badges for restricted rooms (records storage, cash handling, server rooms) plus audit logs that show who entered and when.
- Privacy standards are upheld through consent notices, minimal data collection, clear retention periods, and secure storage aligned with GDPR and CCPA.
- In financial services, visitor management covers vaults and records rooms per GLBA/FFIEC guidance.
- In retail and hospitality, it protects PCI DSS zones, back-of-house areas, and supports crowd management.
- In technology facilities, it delivers SOC 2/ISO 27001 aligned access discipline.
How Can Corporate Teams Set Up Visitor Check-Ins Effectively?
Effective visitor check-in setup requires clear protocols, automated workflows, and scalable processes across corporate and commercial properties:
- Define visitor types and risk tiers—clients, candidates, media, vendors, auditors, VIPs—and assign appropriate escort requirements and access zones.
- Enable pre-registration workflows with host approvals for high-risk visitors and high-volume events.
- Issue time-bound badges with zone restrictions and automatic expiration linked to access control systems.
- Standardize sign-out procedures and reporting to maintain current rosters and exportable compliance documentation by site, tenant, or region.
- Ensure accessibility and experience through clear signage, ADA-compliant processes, multilingual support, and brand-consistent communications.
This structured visitor management approach maintains security standards, streamlines front-desk operations, and generates audit-ready documentation for corporate stakeholders.
? FAQs for Visitor Management in Corporate & Commercial
What counts as a visitor in corporate facility management?
Any non-employee entering a facility—clients, tenant guests, vendors, delivery personnel, auditors, job candidates, media representatives, and escorted guests.
Do visitors need safety briefings at corporate facilities?
Yes, based on access location. Most corporate sites require basic life-safety acknowledgments; restricted areas may require additional PPE, escort protocols, or photography restrictions.
How long should visitor records be kept?
Retention periods should align with internal policies, audit cycles, and privacy regulations. Many organizations set retention schedules based on visitor type and regional compliance requirements.
How does visitor management support emergency evacuations?
Real-time visitor rosters enable accurate headcounts during emergency mustering and roll calls, ensuring all occupants—not only employees—are accounted for during evacuations.
Why are paper sign-in sheets inadequate for corporate environments?
Paper logs expose visitor information at reception desks, are easily lost or damaged, and make it difficult to verify access to sensitive areas or produce multi-site audit reports.
What are the advantages of cloud-based visitor management systems?
Cloud platforms centralize multi-site oversight, integrate with access control and communication systems, enforce policy acknowledgments and watchlist screening, and generate searchable audit trails—while maintaining efficient front-desk operations.

Chapter 4
Why Do Corporate Businesses Need Contractor Compliance Management?
Corporate and commercial organizations need contractor compliance management to ensure every vendor and trade professional working on-site is qualified, insured, and briefed before work begins—protecting people, property, data, and the brand. Corporate and commercial spaces are occupied environments: janitorial crews work near employees, elevator technicians operate in public lobbies, audiovisual (AV) teams access boardrooms, and renovation crews share floors with tenants and guests. If training, certifications, permits, or insurance lapse, organizations risk injuries, code violations, unplanned closures, and costly claims. Centralized oversight makes sure only cleared contractors work on the premises and creates a defensible record of what standards were enforced.
How Do Corporate Teams Manage Contractor Compliance Documents?
Corporate and commercial sites manage contractor compliance documentation by collecting required records, tracking expirations, and tying approval status to site access—using one of four common approaches:
Some sites still rely on binders or file cabinets to store contractor credentials. This approach is prone to lost documents, inconsistent updates, and long retrieval times during audits.
Spreadsheets or Excel, which allows for more organization but requires manual follow-up, is error-prone, and becomes unmanageable across sites.
Standalone software or desktop tools provide more structure for tracking documents, but often lack automation or integration with site check-in systems.
Cloud-based contractor compliance management systems centralize all contractor documents, with required limits and endorsements, licenses, NDAs, and permits; automate reminders for expirations; and link contractor status directly to check-in.
Any method can "store a file." The difference is whether the system enforces policy at the door, scales across portfolios, and produces evidence in seconds when regulators, insurers, or landlords request it.
What Are the Core Tasks of Contractor Compliance Management in Corporate & Commercial Industries?
The core tasks of contractor compliance in corporate and commercial facilities focus on clearing every outside worker before tools or materials reach the site:
Core contractor compliance tasks:
- Collecting and verifying required documents such as licenses, training, and keep an audit trail.
- Set site-specific requirements by contractor type and risk.
- Track expiration dates with reminders to contractors and facility teams.
- Link compliance status to check-in so only approved contractors access the site.
When supported by technology, these tasks extend further:
- Centralized document storage providing a single source of truth across all facilities and eliminating disorganized tracking.
- Automated expiration tracking with real-time notifications to prevent lapses.
- Central dashboards and cross-site visibility into vendor and contractor status.
- Visitor management system integration to auto-approve at sign-in for fast, authorized check-ins.
- Audit-ready recordkeeping with complete, time-stamped history.

How Does Contractor Compliance Management Support Regulations?
Contractor compliance management supports regulations and standards by proving that workers are qualified, insured, and operating under clear controls. Corporate sites must follow OSHA requirements, local fire and building codes, and NFPA rules for hot work. Different industries have specific obligations:
- Financial services align vendor access with GLBA and FFIEC guidance
- Retail and hospitality protect PCI DSS zones and exit routes
- Technology facilities follow SOC 2 and ISO 27001 practices for contractor access
- Multi-tenant properties must meet lease agreements and insurance requirements
How Can Corporate Teams Set Up Contractor Compliance Management Effectively?
Corporate teams can set up contractor compliance effectively by building a program that enforces rules automatically and scales across locations:
- Define categories and risks (cleaning, security, mechanical/electrical/plumbing (MEP) trades, IT/low-voltage, renovation crews, rigging) with requirements per zone (data rooms, records areas, kitchens, rooftops).
- Digitize submissions and approvals; require vendor self-service portals for COIs, licenses, and training proofs.
- Automate expirations with reminders and lockouts when documents lapse.
- Integrate with visitor management so only approved contractors can be badged and scheduled (including docks, elevators, after-hours access).
- Keep audit-ready reports and exception workflows aligned to landlord, insurer, and tenant obligations.
This approach prevents risky on-site work, shortens lobby time, and proves due diligence when it matters most.
? FAQs for Corporate Contractor Compliance Management
What documents are typically required for contractor compliance?
COI with required limits/endorsements, trade licenses, OSHA or role-specific training, W-9/vendor setup forms, NDAs, background checks for sensitive areas, and job-specific permits.
How do multi-tenant buildings keep standards consistent?
Multi-tenant buildings use a building-level rule set in a shared system; allow tenants to add stricter requirements for their suites while preserving a single audit trail.
How can contractors clear access faster?
Contractors can clear access faster by pre-approving documentation before the visit, linking approval to the badge profile, and using pre-registration QR codes at check-in.
What about after-hours or high-impact work?
After-hours or high-impact work requires explicit approvals with start/stop windows, escort rules, noise/dust controls, and proof of post-work inspections before reopening areas.
How is audit readiness maintained for contractor compliance?
Audit readiness is maintained through centralized digital records with time-stamped approvals, permit logs, and access history—exportable by site, vendor, date range, or permit type.
Why are spreadsheets and paper risky for contractor compliance management?
Spreadsheets and paper are risky because they rely on manual follow-ups, don't scale across portfolios, and fail to enforce access rules at the door.
Explore More Contractor Compliance Management Resources

Chapter 5
Why Does Corporate & Commercial Need Emergency Preparedness?
Corporate and commercial organizations need emergency management to quickly alert, direct, evacuate, or shelter all occupants—employees, tenants, guests, and contractors—while accounting for everyone and meeting life-safety and business-continuity requirements. Office buildings, branch locations, retail stores, hotels, event venues, and high-rise properties face diverse emergency scenarios including fire alarms, medical events, utility outages, severe weather, hazardous conditions, and security threats. A structured emergency management program protects people, minimizes disruption, and generates the documentation that regulators, insurers, and property owners require.
How Do Corporate Businesses Manage Emergencies and Preparedness?
Corporate and commercial sites manage emergencies by combining written procedures with technology that accelerates communication and accountability. While paper rosters and radio calls still exist at some facilities, they are slow and incomplete when managing multiple floors or buildings. Modern emergency management programs include:
Some still rely on Paper rosters & radio check-ins to account for people during evacuations. This creates delays, missed headcounts, and incomplete records that fail during audits.
Spreadsheets improve organization but still require manual data entry, lack consistency across multiple sites, and does not support real-time accountability.
Standalone software speeds alerts and musters but often operates in silos without linking to access control or visitor systems.
Cloud-based emergency systems provide centralized oversight, real-time evacuation tracking, mass notifications, and integration with security and compliance tools.
What Are the Core Tasks of Emergency Preparedness in Corporate & Commercial Industries?
Emergency management core tasks ensure that plans function under pressure and that compliance records demonstrate preparedness:
Core emergency preparedness tasks:
- Defining emergency roles and responsibilities for supervisors, floor leaders, and safety officers.
- Mapping muster points and building sweep routes.
- Scheduling and documenting drills to meet regulatory requirements.
- Capturing attendance, headcounts, response times, and all-clear confirmations.
- Reviewing drill and incident performance to identify gaps and corrective actions.
When supported by technology, these tasks extend further:
- Automated mass notifications with two-way messaging via SMS, email, or calls.
- Real-time digital musters and roll calls across multiple muster points.
- Live dashboards showing who is on premise across one or many buildings.
- Reconciliation of headcounts with integrated data from visitor management systems.
- Exportable drill and incident reports to ensure records remain current.
- Building sweeps that divide the site into zones, ensuring systematic and focused safety checks for an organized and efficient evacuation process.

How Does Emergency Management Support Compliance & Safety?
Emergency management demonstrates an organization's ability to protect people and maintain business continuity when incidents occur. Corporate and commercial facilities are required to maintain written Emergency Action Plans (EAPs), provide occupant training, and conduct regular drills to verify that safe evacuation and sheltering procedures function as intended. Fire codes, building codes, landlord requirements, and industry standards—including GLBA and FFIEC guidance for financial facilities, PCI DSS for retail environments, and SOC 2 and ISO 27001 for technology sites—all mandate documented readiness, accurate occupancy lists, and rapid accountability during emergency events. Digital records that capture who was notified, when areas were cleared, and how issues were resolved provide clear, auditable proof of compliance.
How Can Corporate Teams Set Up Emergency Preparedness Effectively?
Building an effective program requires both planning and practice:
- Define site-specific scenarios and document procedures for each.
- Assign roles and responsibilities across security, facility, and safety teams.
- Communicate muster points and establish digital roll call processes.
- Schedule and document drills that align with state and federal requirements.
- Review trends across sites and refine procedures to close gaps and strengthen future preparedness.
This approach ensures that emergency preparedness is not a one-time exercise but a continuous, auditable process.
? FAQs for Corporate Emergency Preparedness
How are visitors and contractors accounted for during an evacuation?
By integrating visitor and contractor check-in systems with emergency management dashboards, all non-employees automatically appear in live muster reports and digital roll calls.
Who owns the emergency plan in a multi-tenant building—the landlord or the tenant?
Both parties share responsibility. The building management sets base emergency procedures and coordinates building-wide drills, while individual tenants maintain suite-level emergency plans and warden teams that align with the overall building program.
How often should emergency drills be conducted?
Follow local fire codes and organizational policies. Many office environments conduct at least annual evacuation drills, while higher-risk facilities and high-rise occupancies may require more frequent drill schedules.
What emergency records should be maintained for compliance audits?
Maintain drill schedules, automated notifications sent, headcount logs with timestamps, evacuation completion times, exception lists with corrective actions, emergency warden rosters, and training attestations.
When is shelter-in-place used instead of building evacuation?
Shelter-in-place procedures apply when leaving the building creates greater risk than remaining inside—during severe weather events, external hazardous material releases, or specific security threats—using pre-written messages and designated interior refuge areas.
Why are manual roll calls risky for corporate and commercial facilities?
Paper-based attendance lists become outdated quickly and typically miss non-employee occupants. Digital rosters update in real time from access control and visitor systems and generate exportable compliance reports for regulators and insurance carriers.
Explore More Emergency Management Resources

Chapter 6
Why Do Corporate Businesses Need Asset & Logistics Tracking?
Corporate and commercial organizations need asset and logistics management to keep high-traffic workplaces, retail stores, hotels, event venues, and multi-tenant buildings properly supplied, accountable, and audit-ready, thereby, ensuring the right items reach the right locations at the right time with documented chain of custody.
In corporate settings, daily material flows include parcels and packages, Information Technology (IT) hardware, audiovisual equipment, records boxes, vendor materials, event equipment, uniforms, and high-value tools.
Without proper oversight, facilities experience lost packages, congested loading docks, delayed projects, privacy exposure from mishandled documents, and safety hazards in loading bays and service corridors. Standardized tracking and dock scheduling prevent operational bottlenecks, protect people and property, and preserve the professional brand experience.
How Do Corporate Businesses Manage Assets & Logistics?
Corporate and commercial sites manage assets and logistics using methods that range from manual processes to fully integrated digital platforms:
Paper logs and clipboards are still common for recording tool check-outs or deliveries, but prone to errors, loss, and illegible handwriting.
Spreadsheets offer better organization but require manual updates, which become unreliable as networks scale.
Legacy point solutions provide digital tracking for specific workflows like mailrooms but often operate in isolation from other systems.
Cloud-based asset and logistics systems data across receiving, storage, usage, and outbound. These systems integrate with ERP or WMS, and use barcodes to track location, condition, and movement in real time with audit-ready trails.
Manual methods can capture basic transaction events, but integrated digital platforms provide verifiable proof of what happened, when it occurred, and who signed for each item, across the entire facility portfolio.
What Are the Core Tasks of Asset & Package Tracking for Corporations?
Effective asset and logistics programs manage the complete item lifecycle within the property.
Core asset & logistics tasks:
- Receiving packages and parcels with accurate documentation.
- Tracking package and parcel movements with searchable chain-of-custody records.
- Managing internal logistics assets such as IT devices, audiovisual equipment, tools, and loaners.
- Controlling storage and access to regulated or high-value items.
- Capturing exceptions for damage, loss, or discrepancies.
- Monitoring condition for sensitive goods when required.
When supported by technology, these tasks extend further:
- Real-time package tracking with barcode scanning that captures custody transfers.
- Digital asset check-in and check-out with automated due dates and overdue alerts.
- Zone-based storage controls that restrict access and log entries.
- Condition monitoring with photo documentation and automated notifications.
- Integration with ERP and other tools to synchronize asset and custody data.
- Exportable chain-of-custody reports for compliance and insurance reviews.

How Does Asset & Package Tracking Support Compliance and Safety?
Asset and package tracking supports compliance and safety by maintaining clear custody records and reducing operational risks. Documented handling procedures keep loading docks and storage areas safe, protect sensitive materials, and demonstrate proper access controls for back-of-house spaces.
Different industries face specific requirements, for example, financial firms must track records according to GLBA standards, retail and hospitality sites need PCI DSS-aligned equipment handling, and technology companies require SOC 2-friendly custody procedures. Complete custody trails showing who handled items, where they were stored, and when they moved provide the documentation needed for insurance claims, audits, and compliance reviews.
How Can Corporations Set Up Asset & Logistics Effectively?
Effective asset and logistics management setup requires clear item categories, defined ownership responsibilities, and documented movement paths:
- Define item categories with custodians and retention rules.
- Map storage zones and paths with access restrictions.
- Use smart lockers or scheduled windows to reduce queues.
- Integrate digital systems including ERPs, smart lockers, and more.
- Codify exception procedures with notes and approvals.
This structured approach to asset and logistics management reduces item loss, shortens delivery cycle times, and creates exportable documentation for compliance audits.
? FAQs for Corporate & Commercial Logistics Management
What is the difference between assets, inventory, and packages?
Assets are owned resources used to operate the facility including laptops, audiovisual kits, and maintenance tools. Inventory represents stock items for sale or consumption. Packages are individual shipments moving through the property from external sources.
Should employees be allowed to receive personal parcels at corporate facilities?
Organizations should establish clear policies. Many companies restrict personal package delivery to reduce liability exposure, lobby congestion, and privacy risks associated with handling personal items.
Do facilities need mobile scanning capabilities for asset tracking?
Yes—barcode scans at receiving dock, storage locations, and final delivery points significantly improve tracking accuracy and speed while producing reliable chain of custody documentation.
How should return shipments be handled?
Establish a reverse logistics workflow including item pickup, verification against original records, re-labeling, carrier hand-off, and proof of dispatch—all logged against the original receiving record.
How should return shipments be handled?
Establish a reverse logistics workflow including item pickup, verification against original records, re-labeling, carrier hand-off, and proof of dispatch—all logged against the original receiving record.
Who owns custody responsibility for tenant-specific items in multi-tenant commercial buildings?
Building management typically oversees loading dock operations and base building custody procedures, while individual tenants maintain suite-level custody responsibility and approval authority. A shared tracking system preserves one unified audit trail.
Explore More Logistics Management Resources

Chapter 3
Why Do Corporations Need Identity & Access Management?
Corporate and commercial organizations need identity and access management to control who can enter specific rooms and when—protecting people, assets, and confidential information while creating records for audits and compliance reviews. These properties mix public spaces like lobbies with restricted areas such as storage rooms, vaults, trading floors, server rooms, laboratories, cash offices, stockrooms, back corridors, control rooms, rooftops, and equipment spaces. Without proper access controls, facilities risk theft, data breaches, safety incidents, and compliance violations.
How Do Corporations Manage Physical Identity and Access?
Corporate and commercial sites use identity and access management approaches ranging from manual key systems to integrated Physical Identity and Access Management (PIAM) platforms:
Manual sign-in and key distribution is still used in smaller sites, but risky due to lost keys, lack of tracking, and no audit trail.
Standalone badge systems provide basic access controls, but often lack integration with HR systems or visitor check-ins.
On-premise PIAM solutions assign permissions more systematically, but can be difficult to scale across multiple sites.
Cloud-based identity and access management systems automate provisioning, enforce role- and zone-based permissions, making compliance and oversight easier.
Modern identity and access management programs also link access prerequisites including required training certifications, signed non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), and background check clearances to door permissions so unqualified individuals cannot badge into restricted areas.
What Are the Core Tasks of Access Management in Corporate & Commercial Sites?
Identity and access management core tasks verify user identity, assign least-privilege access permissions, and maintain clean compliance records:
Core access management tasks:
- Identity proofing and pre-approval for employees, contractors, vendors, and guests.
- Role- and zone-based permissions aligned to risk levels and business hours.
- Issuing temporary, time-boxed badges with escort or area restrictions as needed.
- Managing badge lifecycles, including issuance, updates, suspensions, and revocations.
When supported by technology and visitor management integration, these tasks extend further:
- Role-based access control that applies time-bound permissions and prevents unauthorized entry to restricted areas.
- Dynamic credential management with automatic expiration, escort requirements, and real-time provisioning or revocation.
- Real-time monitoring and alerts for denied access, tailgating, and credential misuse.
- Centralized dashboards and reporting with exportable logs and analytics across the portfolio.

How Does Visitor Management Support Compliance and Safety?
Identity and access management systems provide clear records showing that the right people accessed the right areas at the right times. These systems help facilities meet two main compliance needs: keeping people safe and protecting sensitive information. For safety, access controls prevent unauthorized entry to dangerous areas like mechanical rooms, rooftops, and kitchens, while also tracking who's in the building during emergencies. For security and privacy, different industries have different requirements—financial companies must control access to vaults and secure records, retail and hospitality sites need to protect payment processing areas and cash offices, and technology companies must secure server rooms and research labs.
Digital access logs that show who entered restricted areas, when they entered, and under what authority provide the documentation needed for audits, regulatory reviews, and security assessments.
How Can Corporations Set Up PIAM Systems Effectively?
Implementing physical identity and access management requires a structured process that can be applied consistently across sites:
- Define user roles and access zones with time-based permissions and prerequisite requirements.
- Automate credential provisioning with rule-based workflows for visitors and contractors.
- Issue temporary credentials with automatic expiration for daily, recurring, or event-based access.
- Control entry points by specifying which doors, gates, or areas each credential can access.
- Monitor access in real time with digital audit logs and comprehensive reporting across all locations.
? FAQs for Access Control in Corporations & Commercial Sites
What is the difference between PIAM and traditional access control?
Traditional access control manages doors and locks for employees. Physical Identity and Access Management (PIAM) extends these systems to handle visitors, contractors, and temporary guests. SecurityOS, for example, automates credential provisioning with rule-based workflows, issues time-limited credentials with zone-specific permissions, and maintains digital audit logs of all temporary access across your facility portfolio.
How does identity and access management handle temporary contractors and visitors?
A PIAM system like SecurityOS issues time-limited credentials with customized permissions for specific entry points and time windows. Credentials can be configured to expire automatically on sign-out or after a set duration, eliminating manual revocation steps. The system integrates with your visitor management workflows to automate the provisioning process.
Should corporate facilities use mobile credentials instead of physical badges?
Mobile credentials offer faster provisioning, automatic expiration, and remote revocation capabilities. SecurityOS can deliver credentials via QR code for temporary access scenarios. However, organizations should maintain multiple credential options to accommodate visitors, contractors, and employees with different device capabilities and preferences.
How often should access permission reviews be conducted?
Most corporate and commercial organizations conduct quarterly or semi-annual access recertification reviews for high-risk zones including server rooms, vaults, records storage, and rooftops. Standard office access may be reviewed annually. The review cadence should align with regulatory requirements, tenant lease obligations, and internal audit schedules. SecurityOS provides comprehensive reporting and digital audit trails to support these review processes.

Chapter 8
Compliance and the Regulatory Landscape
Corporate and commercial facility leaders face a complex compliance environment: building codes, workplace regulations, privacy laws, and industry-specific standards. Every office, retail location, hotel, financial services branch, and multi-tenant portfolio must satisfy all of them simultaneously. The operational challenge is proving, consistently and in real time, that you're following them.
The systems you deploy generate the evidence trail that auditors, insurers, landlords, and regulators will scrutinize. When compliance controls are embedded directly into your operational platform, your portfolio stays audit-ready by default. The table below maps the regulatory terrain across six common corporate and commercial sectors.
Financial Services (Banking, Finance, Law)
Main Focus: Vault/records access; visitor escorts; audit logs; evacuation tracking; chain of custody
|
United States |
Canada |
Global |
|
GLBA - Customer data security
|
PIPEDA - Data privacy
|
GDPR - Data privacy |
Retail, Grocery & Pharmacies
Main Focus: Crowd control; cash-office security; perishable monitoring; vendor management; dock safety
|
United States |
Canada |
Global |
|
OSHA - Workplace safety |
CFIA - Food safety |
PCI DSS - Payment security ISO 22000 - Food safety HACCP - Hazard control |
Hospitality & Lodging
Main Focus: Guest/staff separation; kitchen testing; evacuation drills; key control; contractor permits.
|
United States |
Canada |
Global |
|
OSHA - Worker safety |
Canada Labour Code - Health & safety |
ISO 45001 - Health & safety |
Real Estate & Property Management (Multi-Tenant)
Main Focus: On-site visibility for mixed Life-safety systems; hot-work permits; access control; tenant coordination; dock management
|
United States |
Canada |
Global |
|
IBC/IFC - Building & fire codes
|
Building & Fire Codes |
ISO 41001 - Facility management
|
Technology & Software / Data-Intensive Sites
Main Focus: Server/lab access; NDA capture; visitor monitoring; asset custody; 24/7 procedures
|
United States |
Canada |
Global |
|
CCPA/CPRA - Privacy rights |
PIPEDA - Privacy law |
GDPR - Data privacy
|
Media, Entertainment & Venues
Main Focus: Credentialed zones; crowd management; emergency plans; permits; headcount tracking
|
United States |
Canada |
Global |
|
NFPA/IBC/IFC - Public assembly safety |
Building & Fire Codes - Venue safety |
ISO 22320 - Emergency management
|
Why Is Compliance Tied to Facility Management?
Compliance and facility operations are inseparable. The same systems that manage daily activities—visitor check-ins, contractor approvals, emergency response, asset tracking, and access control—automatically generate the evidence that regulators and landlords require. Check-in workflows capture identity verification and acknowledgments. Contractor portals confirm insurance, permits, and training. Emergency programs log notifications, muster times, and all-clear events. Asset tools maintain chain-of-custody. Access platforms record who entered which zones and when.
When these controls are embedded in daily routines rather than treated as separate "audit prep" tasks, inspections become faster, audit findings decrease, and brand trust strengthens. Strong facility systems transform regulatory requirements into repeatable workflows that keep sites audit-ready while building a foundation for continuous digital improvement.

Chapter 9
Technology & Digital Transformation in Facility Management
Corporate and commercial facility teams are transitioning from manual, improvised tools to integrated digital platforms that standardize operations across offices, branches, retail locations, hotels, event venues, and multi-tenant buildings. This shift toward facility management software strengthens oversight, protects privacy and safety, and maintains consistent customer and employee experiences that align with brand standards.
How Is Corporate Facility Management Shifting from Manual to Digital?
Many corporate locations rely on paper visitor logs, physical insurance binders, spreadsheet permit trackers, and radios during drills. These manual methods fail when portfolios expand or auditors request historical records across multiple buildings. Digital facility management platforms replace manual tools with cloud-based systems that standardize workflows and provide real-time visibility. In privacy-sensitive settings, digital records reduce exposure by limiting PII access and automatically enforcing retention policies.
What Are the Benefits of Facility Management Software for Corporations?
Implementing integrated facility management software fundamentally changes how buildings operate and how easily organizations demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements:
Automated Compliance Workflows
Systems trigger reminders for expiring contractor insurance, display required acknowledgments at check-in, and enforce hot-work permit procedures.
Enhanced Lobby Experience
Pre-registration, digital badges, and streamlined check-in processes reduce lobby wait times and create professional, brand-aligned first impressions across all locations.
System Integrations
A facility management platform that integrates all essential facility operations like visitor, emergency, contractor compliance, logistics, and access management.
Operational Analytics
Dashboards reveal approval bottlenecks, security alarm patterns, lobby traffic peaks, and evacuation variances across office buildings, retail locations, and commercial properties.
Privacy & Brand Protection
Digital workflows minimize PII exposure at reception desks, enforce data retention policies, and maintain consistent corporate brand experiences.
Why Facility Management Software Matters for Corporate & Commercial?
Corporate and commercial environments are inherently distributed and dynamic, with continuous activity including new employee onboarding every week, rotating vendor relationships, seasonal retail volume peaks, tenant construction projects, VIP events, and hybrid work attendance patterns. Facility management software does not replace organizational policy—it codifies and enforces it consistently. Role-based access rules, zone-specific permissions, time-bound digital badges, loading dock time windows, and visitor pre-registration approval workflows become embedded in daily operations rather than relying on manual reminders and staff memory.
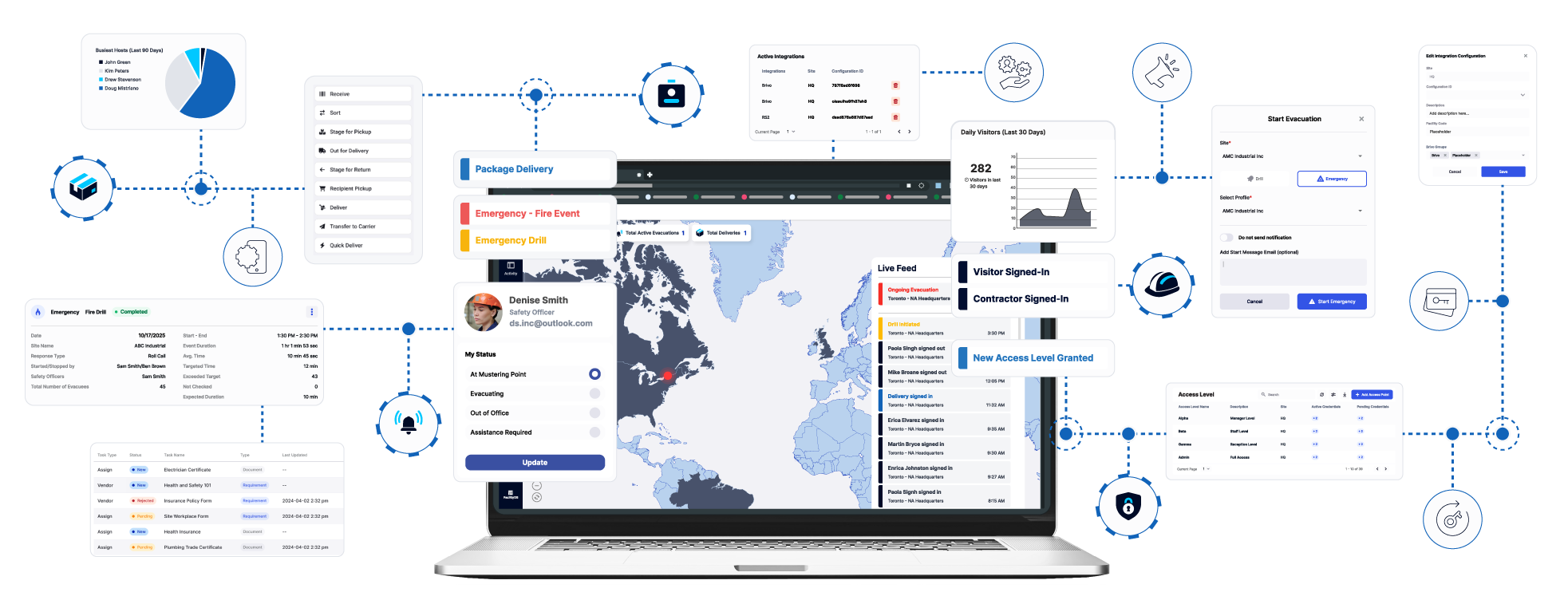
One platform that addresses these needs is FacilityOS, which offers modular solutions for visitor management (VisitorOS), emergency and evacuation management (EmergencyOS), contractor compliance (ContractorOS), asset and logistics management (LogisticsOS), and physical identity and access management (SecurityOS). Logistics operations can start with one module and expand as their needs evolve, ensuring scalability across single sites or entire networks while maintaining a unified user experience and centralized reporting.
Related Resources

Chapter 10
Measuring Success: KPIs for Facility Management
Corporate and commercial facility managers need measurable data to demonstrate that safety protocols, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency are improving across their portfolios.
The right facility management KPIs transform daily operational activities into actionable metrics that satisfy portfolio owners, property landlords, insurance auditors, and regulatory inspectors.
What Are Key KPIs in Facility Management for Corporate Businesses?
Facility management KPIs provide corporate and commercial leaders with a clear way to measure compliance, safety, efficiency, and visibility across their operations. Build performance measures that match your risks, goals, and workflows. Use this approach:
Define Outcomes & Requirements
Identify key results (fewer incidents, faster evacuations, audit readiness) and link them to applicable regulations.
Map Workflows
Connect outcomes to the processes that drive them: visitor check-in, contractor credentialing, emergency drills, access control, and logistics tracking.
Select Metrics
Choose leading indicators (% visitors pre-registered, % drills completed on time) and lagging indicators (evacuation times, access violations) that you can capture automatically.
Set Definitions & Targets
Write clear definitions, assign owners, establish thresholds, and set goals by building, department, or campus type.
Pilot and Refine.
Test metrics at one site, confirm they respond to process improvements, and retire any that don't drive action.
Standardize & Improve
Roll out common metrics across locations, review regularly in safety committees, and assign corrective actions to demonstrate continuous improvement.
Quick test: A KPI is useful if a facilities lead or property manager can explain how to improve it today and if the data is available in real-time.
Why Are KPIs Important in Facility Management?
Facility management KPIs transform operational assumptions into verified evidence. These metrics clearly demonstrate whether safety controls are functioning effectively, identify where policy enforcement breaks down across multiple locations, and reveal which sites require additional operational support or training. KPIs help facility managers justify reception staffing levels, prioritize physical access control system upgrades, and prove that vendor management policies are applied consistently across entire corporate portfolios. For customer-facing commercial spaces, facility management KPIs also quantify the quality of visitor experiences through metrics like reduced lobby wait times, fewer delivery failures, and faster issue resolution.
How Do KPIs Show ROI in Facility Management?
Strong facility management KPIs deliver measurable cost savings and risk reduction across corporate and commercial portfolios. Benefits include fewer safety incidents and insurance claims, faster regulatory audits requiring less preparation time, reduced staff overtime from operational rework at loading docks or reception desks, lower inventory shrinkage and asset loss, and improved tenant or guest satisfaction scores. When facility management leaders can demonstrate higher compliance rates, faster emergency evacuation times, and complete chain-of-custody documentation, justifying investment in modern facility management systems becomes significantly easier for executive stakeholders.

Chapter 11
Future of Corporate & Commercial Facility Management
Continuous compliance means maintaining inspection-ready facility operations every single day rather than scrambling before scheduled audits or landlord reviews. Visitor acknowledgments, contractor certificates of insurance, access permission approvals, emergency drill documentation, and permit close-out records are automatically captured as operational activities occur. Real-time facility management dashboards immediately flag compliance lapses—such as expired insurance endorsements, missed fire warden training drills, or overdue permit close-outs—enabling facility teams to correct issues quickly and maintain consistent compliance standards across all portfolio locations and tenant spaces.
What Is Continuous Compliance in Corporate Facility Management?
Continuous compliance means maintaining inspection-ready facility operations every single day rather than scrambling before scheduled audits or landlord reviews. Visitor acknowledgments, contractor certificates of insurance, access permission approvals, emergency drill documentation, and permit close-out records are automatically captured as operational activities occur. Real-time facility management dashboards immediately flag compliance lapses—such as expired insurance endorsements, missed fire warden training drills, or overdue permit close-outs—enabling facility teams to correct issues quickly and maintain consistent compliance standards across all portfolio locations and tenant spaces.
How Can Future AI Improve Facility Management in Corporations?
AI-powered facility management systems analyze operational data to provide actionable insights and recommendations:
- Risk detection and signals. Identify unusual access patterns, repeated permit violations, or chronic door-held security alarms by specific time periods and building zones.
- Staffing optimization and traffic flow. Accurately forecast lobby traffic peaks or loading dock congestion periods and recommend proactive staffing schedule adjustments.
- Compliance monitoring and hygiene. Detect credential permission creep, identify contractors likely to experience documentation lapses, and recommend proactive outreach before compliance issues occur.
- Incident analysis and insights. Automatically summarize emergency drill reports and after-action documentation, highlighting evacuation bottlenecks that delay safe building re-entry procedures.
- Asset efficiency optimization. Analyze utilization patterns for shared IT equipment and AV resource pools to recommend optimal inventory levels.
- Built-in AI assistants. Get more value from the software by answering how-to questions, suggesting next best actions, and highlighting the insights that matter most for each role.
What Is System Integration in Corporate Facility Management?
Facility management system integration connects different operational tools so that when something happens in one system, related systems update automatically. Here are some examples:
- A host pre-registers a guest, and the system automatically creates a visitor badge with the right access permissions
- A contractor's insurance expires, and their building access is immediately suspended
- A fire alarm goes off, triggering emergency notifications, pulling real-time occupancy lists, and starting digital muster procedures
- A package arrives and scans into a smart locker, instantly sending the recipient a pickup code
Integrated facility management platforms connect many systems—including HRIS, physical access control, visitor and contractor portals, loading dock scheduling, mailroom and smart lockers, building management systems, fire alarm panels, asset management tools, and communication platforms. Together, they create a single, auditable record that shows what happened, when it happened, and who approved it.
The future of corporate and commercial facility management is moving toward operations that are easier to manage: controls built into daily work, real-time dashboards for quick decisions, and connected systems that reduce paperwork while improving safety, compliance, and the experience for everyone who walks through the door.
Conclusion
Final Thoughts on Corporate Facility Management
Corporate and commercial properties operate in complex environments where occupant safety, regulatory compliance, and consistent customer or employee experiences are non-negotiable business requirements. Professional facility management provides the operational structure that protects people, secures physical spaces and sensitive data, and keeps business locations operational across diverse property types including corporate offices, retail branches, hotels, event venues, and multi-tenant commercial buildings.
Well-designed facility management processes supported by integrated digital platforms reduce lobby wait times, standardize contractor vetting procedures, generate accurate real-time occupancy rosters during emergency incidents, and maintain complete chain-of-custody documentation for packages and shared facility assets. These operational controls streamline regulatory inspections, ensure consistent safety training and policy acknowledgments, and guarantee that restricted building areas are only accessed by properly authorized individuals at appropriate times.
By investing in integrated, well-documented facility management operations, corporate and commercial organizations achieve benefits far beyond basic regulatory compliance. They build operational resilience across entire property portfolios, minimize business disruption during high-volume periods and construction projects, and strengthen trust relationships with employees, commercial tenants, guests, clients, and insurance providers.
? FAQs About Facility Management in Corporations
How does maintenance fit into facility management?
Maintenance is one part of facility management, not the whole program. Facility operations also include visitor oversight, contractor compliance, emergency preparedness, identity and access control, and asset and logistics management. Maintenance keeps equipment working. Facility management keeps the entire location safe, compliant, and audit-ready.
What roles are involved in corporate facility operations?
A Facility or Property Manager coordinates daily operations. An EHS or Life-Safety lead manages drills, plans, and compliance. A Security Officer manages access, credentials, and incident response. Front desk or lobby teams handle check-ins. IT and Workplace or Building Systems teams maintain integrations with access control, communications, and asset tools. Together they keep sites safe, consistent, and efficient.
What technology is recommended for corporate facility management?
Integrated platforms that replace manual logs with connected workflows. For example, FacilityOS modules can manage visitor check-ins (VisitorOS), contractor documentation and permits (ContractorOS), emergency preparedness and musters (EmergencyOS), identity and access control (SecurityOS), and packages, docks, and shared assets (LogisticsOS). One platform reduces gaps, provides real-time visibility, and keeps locations audit-ready.


